carried over-Attachment B-2 Directory 2016-17 to 2018-19
EDFacts Data Collection School Years 2019-20, 2020-21, and 2021-22 (with 2018-19 continuation)
carried over-Attachment B-2 Directory 2016-17 to 2018-19
OMB: 1850-0925
Paperwork Reduction Act Submission Supporting Statement
Annual Mandatory Collection of Elementary and Secondary
Education Data through EDFacts
February 2016
Attachment B-2
Directory Records for the EDFacts Data Set
for School Years 2016-17, 2017-18, and 2018-19
Introduction
This attachment explains the data collected to define education units referred to as the directory. All data collected through EDFacts are linked to education units in the directory. This attachment also explains the data collected for a roster of charter school authorizers. Each charter school is linked to an authorizer.
In previous clearance packages the information on the directory and the roster of charter school authorizers was included in the Overview attachment. The information on directory and the roster of charter schools has been separated out in this clearance packages so that the information is easier to review.
This attachment is organized into two main sections as follows:
Section 1 – Explanation of the Directory
What is the directory
How are directory data used
Why changes are being proposed
How the directory is organized
Section 2 – Data Collected
About the directory, EMAPS metadata survey
For the directory of SEAs, LEAs and schools, FS 029 Directory
For the roster of charter school authorizers, FS 190 Charter Authorizer Roster
There are three appendices for this attachment:
Appendix A – Definition of LEA from the Code of Federal Regulations
Appendix B – Files submitted at the school level
Appendix C – Some of the data derived from the directory data submitted by the states
The Overview (Attachment B-1) contains a list of acronyms used in the clearance package.
Tips for Reviewing this Attachment The terms used in this attachment may be different than the terms used in any particular state. The section “How the directory is organized” contains the definitions of terms used in this attachment. This attachment includes more explanation of the directory data than was found in previous clearance packages. Changes to the data to be collected are marked throughout this document. Items marked as New! (60) or Revised! (60) were added or updated for the 60 day public comment period. Items marked New! (30) or Revised (30!) have been added or updated for the 30 day public comment period in response to the comment feedback received. Items marked as Final have been revised in the final package in response to the 30 day public comment feedback received. The additional explanation of the directory included in this attachment from previous clearance packages is not marked. Reviewers are strongly encouraged to start with section 1 of this document. |
Table of Contents
Publish the official directory and report official statistics 8
Serve as sampling frame for statistical studies 8
Serve as sampling frame for NAEP 8
Define the universe for the CRDC 9
Populate the list of schools used on FAFSA 9
Why Changes Are Being Proposed 10
How the Directory is Organized 12
Local Education Agency Level 12
Regular Public School District 15
Specialized Public School District 16
Independent Charter Districts 18
Career and Technical Education Schools 21
Alterative Education Schools 22
States with Charter Schools 22
Directory reporting requirements for states with charter schools 24
New! Metadata Collected About the Directory 28
For the Directory Of SEAs, LEAs, and Schools 31
Other descriptive information 39
Detailed Description of the Roster 40
Linking Charter Schools to Charter Authorizers 41
New! Charter Management Organizations roster 41
Appendix A – Definition of LEA from CFR 42
Section 1
Explanation of the directory
What is the Directory
At the start of each school year, each state education agency (SEA) submits files containing the data that defines the education units in that state, that is, a directory. The education units in each state are organized into a three-tier hierarchy:
State level
Local Education Agency (LEA) level
School level
The directory records include the following information on each education unit:
Unique identifiers (e.g., name and identification numbers)
Contact information (e.g., addresses)
Descriptive information (e.g., operational status).
Every school is associated with an LEA. Every school and LEA is associated with a state. The state and NCES identifiers link the education units to each other in the hierarchy. That is, the record for each school includes both the state and NCES identifiers of the LEA to which the school belongs. Records for both LEAs and schools include the identifiers of the state.
How Are Directory Data Used
The directory determines the universe for EDFacts. Prior to submitting any other data, a directory record must exist for every LEA and school and every school must be linked to an LEA. If a directory record does not exist, all other data submissions for that educational entity will fail. Therefore, the LEA and school directory files must be the first files submitted for each school year.
Purposes of the directory data include:
Reporting data for U.S. Department of Education grant programs
Publishing the official directory of education units
Reporting official statistics on public education
Identifying rural school districts for the Rural Education Achievement Program (REAP)
Providing list of LEAs and schools for use in the Migrant Student Exchange System (MSIX)
Serving as sampling frame for statistical studies
Serving as sampling frame for National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP)
Defining the universe for the Civil Rights Data Collection (CRDC)
Populating the list of schools used on the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA)
Each state submits the education units needed to completely and accurately report data for all data groups in the EDFacts data set. In some cases, an education unit is used for some purposes (data groups) and not for others.
The rest of this section provides more detail on some uses of the directory data.
Report program data
Attachment B-3 describes in detail the data submitted for U.S. Department of Education grant programs. The directory must include all education units that need to report data for these programs.
The program data submitted populates the Consolidated State Performance Report (CSPR), IDEA Section 618 and other program reports.
The program data submitted are also used in public analysis files.
Publish the official directory and report official statistics
The CCD is designed to be the Department of Education’s comprehensive statistical database of all public schools and school districts. It serves as the basis of official statistics that provide information on the condition of education. Each year NCES “locks” their published directory for the CCD collection. While SEAs can make changes to the directory in ESS after the directory is “locked” for CCD, those changes will not affect the published CCD file and could have unanticipated consequences. Data in the final CCD collection are used in NCES publications, including the annual compendia, the Digest of Education and the Condition of Education.
Serve as sampling frame for statistical studies
The CCD is used as a sampling frame for cross-sectional and longitudinal school-based surveys conducted by NCES. For example, the National Teacher and Principal Survey (formerly the Schools and Staffing Survey), draws a sample of public schools from the most recent CCD file that is available. Longitudinal surveys like the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study (ECLS), the Middle Grades Longitudinal Study (MGLS), and the High School Longitudinal Study (HSLS) also start with the CCD to create a full listing of schools that meet specified grade ranges. Sampled schools are then contacted for participation in the studies. The CCD is used to help produce the sampling weights. CCD variables are used as composite variables in the final data sets, and are used by researchers as control variables in their analyses.
Serve as sampling frame for NAEP
The CCD serves as the public school sampling frame for the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). To annually construct the NAEP sampling frame NCES requires the most current public school information regarding grade spans, enrollment and district affiliation that is consistent both within and across states and jurisdictions of interest. Additionally, using the CCD as the sampling frame allows for NAEP results to be consistently reported with other NCES reports and products that also use CCD data.
Define the universe for the CRDC
The respondent universe of the CRDC will be based on the most recently available data from the Common Core of Data (CCD) National Public Education Survey of Local Educational Agencies (LEA). The CRDC does not include schools and school districts in the outlying areas or overseas Department of Defense schools.
The CRDC is primarily designed to collect data from public school districts about educational entities where students receive educational services for at least 50 percent of the school day, regardless of whether students are reported elsewhere for funding, accountability, or other reporting purposes. To be eligible to participate in the CRDC, schools must serve students at the site for at least 50 percent of the school year. Since the CCD and CRDC differ slightly in scope, some records are deleted, added or modified in order to provide better coverage and a more efficient sample design for the CRDC. Districts with no membership or missing membership at the district level are generally excluded, except in some special cases, such as where membership data were available for the associated schools.
Additionally, OCR augments the CRDC frame with justice facilities, which may not be under the purview of the SEA. In collaboration with the Department of Justice Office for Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention (OJJDP), OCR adds justice facilities which may not have been otherwise included in the CCD to ensure coverage of all youth in pre- or post-adjudication facilities that receive educational services. Also, state-operated programs for special populations of students (such as schools for the deaf and schools for the blind) are added to the universe if they are not already included in the CCD.
Populate the list of schools used on FAFSA
The Department’s Federal Student Aid (FSA) program provides an on-line Free Application for Student AID (FAFSA) which helps students pay for their college education. Several years ago, information on high school of graduation was added to the on-line FAFSA. Through regular data sharing between NCES and FSA, the CCD Directory is used to populate the list of high schools presented to students when completing this application. This allows the official identifying and contact information from the CCD for the school to be pulled into the FAFSA record.
Why Changes Are Being Proposed
This section explains why changes are being proposed to the directory data submitted by SEAs for EDFacts. Items marked as New! (60) or Revised! (60) were added or updated for the 60 day public comment period. Items marked New! (30) or Revised (30!) have been added or updated for the 30 day public comment period in response to the comment feedback received. Items marked as Final have been revised in the final package in response to the 30 day public comment feedback received.
Scope of the directory
To clarify the scope of the directory records submitted by the SEA so that data users understand what education units are included in the directory for each state:
Adding a metadata survey
The survey is explained in the section “Metadata Collected About the Directory.”
Education units in the LEA file
To clarify for SEAs what education units are to be reported in the LEA file and to separate public school districts from other types of LEAs for data users, the following changes are proposed:
Changing the focus from defining local education agency (LEA) to defining each type of LEA
Adding an explanation of the expected reporting requirements for each type of LEA.
Adding a definition for regular public school district
Adding an LEA type of specialized public school district
Changing the name and requirements for the LEA type RESA to exclude LEAs with schools
Dropping the use of the term “education agency” in lieu of LEA1
These changes are explained in the section “How the Directory is Organized.”
Education units in the school file
To clarify for SEAs what education units are to be reported in the school file as schools, the following changes are proposed
Revising the definition of school
Changing the name of Vocational School to Career and Technical School
Revising the definitions of some of the school types
Adding an explanation of the expected reporting requirements for each type of school
These changes are explained in the section “How the directory is organized.”
Operational status of LEAs and schools
The 60 day package contained a section describing a proposed change to operational status (DG 16) which has been withdrawn and is not included in this package.
Virtual schools
To keep the directory file focused on the essential data elements for management of the directory while also providing data users with sufficient information for decisions about sampling frames for statistical surveys, the following changes are proposed to virtual school status (DG 803):
Move data group from the directory to the CCD School File (FS 129)
Expanding the virtual school status from yes/no to:
Full Virtual
Virtual with Face to Face Options
Supplemental Virtual
Not Virtual
This change is explained in Attachment B-3.
Charter schools
The 60 day package included adding a roster of charter management organizations. The data requirements for charter management organizations have been moved to Attachment B-3.
How the Directory is Organized
This section explains the education units that are submitted for the three tiers of the hierarchy used for EDFacts reporting: State level, Local Education Agency (LEA) level, and school level. After the segments on state, LEA, and school levels, there is a segment explaining directory reporting unique for states that have charter schools. The final segment is a summary.
Each state fits its unique set of education units into this three-tier hierarchy so that the state can accurately and complete report its data.
State Level
The only education unit reported at the state level is the State Education Agency (SEA). The definition of an SEA is in the box below. This is the same definition as the prior package.
-
Definition – State Education Agency (SEA)
A state education agency (SEA) is the agency of the state charged with primary responsibility for coordinating and supervising public elementary and secondary instruction (education), including the setting of standards for instructional programs and is the state agency that administers federal grant programs under the ESEA.
State agencies, other than the SEA, may be involved in “coordinating and supervising public elementary and secondary instruction.” For example, another state agency may administer the programs under Carl D. Perkins Career and Technical Education Act of 2006. But only one state agency is designated as the agency that administers the federal grant programs under the ESEA. The directory record at the state level is for the SEA.
While the directory record at the state level is for the SEA, data submitted at the state level may contain data for other state agencies. For example, if schools or reportable programs are operated by another state agency, such as the Department of Corrections, the SEA should make arrangements with that agency to obtain the data and submit the data.
Local Education Agency Level
Several types of education units are reported at the local education agency level. Agencies reported at this level are education units in a state that are not the State Education Agency and are not schools.
Below is the definition of a local education agency (LEA) from the previous clearance.
-
Definition from Previous Clearance – Public School
A local educational agency (LEA) or educational agency is a governmental administrative unit at the local level which exists primarily to operate schools or to contract for educational services. These units may or may not be coterminous with county, city, or town boundaries.
Unlike prior packages, this package does not focus on the definition of LEA. Instead, this package focuses more comprehensive definitions of each type of LEAs and a summary of the expected reporting for each type. If an organization in a state meets one of the definitions in this section and is required to report data, the organization should be included in the directory at the LEA level.
The definition of an LEA for this package will be based on the definition from the Code of Federal Regulations.
-
Revised! (60) Proposed Definition – Local Education Agency
Local educational agency or LEA means a public board of education or other public authority legally constituted within a State for either administrative control or direction of, or to perform a service function for, public elementary schools or secondary schools in a city, county, township, school district, or other political subdivision of a State, or for a combination of school districts or counties as are recognized in a State as an administrative agency for its public elementary schools or secondary schools.
The full citation from the Code of Federal Regulations is included in Appendix A.
Name |
Local education agency (LEA) type |
|
ID |
453 |
|
Definition Revised! (60) |
The classification of an education unit reported in the local education agency (LEA) file. |
|
Permitted Values Revised! (30) |
||
Previous Clearance |
Proposed |
|
1 – Regular school district that is NOT a component of a supervisory union 2 – Regular school district that is a component of a supervisory union 3 - Supervisory union 4 - Regional education service agency (RESA) 5 - State agency 6 - Federal agency 8 - Other local education agencies
If the state’s legislation for charter schools allows the creation of school districts exclusively for charter schools, then
7-Independent charter district |
1 – Regular public school district that is NOT a component of a supervisory union 2 – Regular public school district that is a component of a supervisory union 3 - Supervisory union 9 - Specialized public school district 4 - Service agency 5 - State operated agency 6 - Federal operated agency 8 - Other local education agencies
If the state’s legislation for charter schools allows the creation of school districts exclusively for charter schools, then
7-Independent charter district |
|
The “Other LEAs” permitted value is available for SEAs that have data to report at the LEA level for an education unit that the SEA has determined is not one of the existing types.
Expected reporting by type
The table below indicates the expected reporting of key date by the type of LEA. Because the type “Other LEAs” is used by SEAs when the SEA determines that there is an entity that needs to be reported and that one of the other types is not appropriate, ED has not defined expected reporting by type for “Other LEAs.”
|
Regular public school districts (1 and 2) |
Supervisory unions (3) |
Specialized public school district (9) |
Service agency (4) |
State operated agencies (5) |
Federal operated agencies (6) |
Independent charter districts (7) |
Have schools |
Yes1 |
No |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
CCD |
|||||||
Membership (FS 052) |
Yes |
No |
Maybe2 |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Graduates (FS 040) |
Yes |
No |
Maybe |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Dropouts (FS 032) |
Yes |
No |
Maybe |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Staff (FS 059) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
CSPR |
|||||||
Assessment |
Yes |
No |
Maybe |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Federal programs |
Yes |
Yes |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Maybe |
CRDC |
Yes1 |
No |
Yes |
No |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Yes |
Footnotes |
1 In a few situations, a regular public school district tuitions all students to schools that are not operated by the district. In these cases, the regular public school district will not have any schools and would not report to CRDC. |
||||||
2 Specialized public school districts could consist of all shared time schools, thus the specialized public school district would have schools but no students reported in membership (FS 052). |
|||||||
For CCD, students are reported at the LEA level by their home district. For CRDC, students are reported based on student location.
Regular Public School District
All states have regular public school districts; therefore, all states submit records on the regular public school districts in their states.
-
Revised! (60) Proposed Definition – Regular Public School District
A regular public school district is a local government administrative authority which governs the education system at a specified local level on behalf of the public and the state.
Under this definition, a regular public school district:
Is state authorized, either directly or through delegated authority
Is governed in accordance with state statute (e.g., a publically elected school board)
Designs and develops education standards and goals, including curriculum in support of state guidelines
Is authorized to provide education credentials1
Has primary responsibility for providing public education
Has a superintendent who is either appointed or elected
Has one or more schools that it manages or operates OR tuitions all students
Procures and allocates funding from federal, state and local sources for schools and other education and related services
Regular public school districts are reported as either:
Regular public school district that is not a component of a supervisory union
Regular public school district that is a component of a supervisory union
Supervisory Union
States that have supervisory unions submit records on those education units in the LEA level file.
-
Definition – Supervisory Union
A supervisory union is an administrative center or county superintendent’s office serving as the administrative center.
Not all states have supervisory unions. The state may use a different name for these entities. As explained later in this attachment, states with supervisory unions include the supervisory union identifier in the file to link the regular public school districts to the supervisory union.
Specialized Public School District
Some states have school districts that are designed for a specific need or purpose. For example, a state would report specialized public school districts if the state has school districts with only career and technical schools. These districts may serve a geographic region that encompasses multiple regular public school districts. If the state has such entities, then the state submits records on those education units in the LEA level file.
-
New! (60), Revised! (30) Proposed Definition – Specialized Public School District
A specialized public school district is a school district that operates one or more schools that are designed for a specific educational need or purpose.
Not all states have specialized public school districts.
Under this definition, a specialized public school district: Final
Is state authorized, either directly or through delegated authority
Is governed in accordance with state statute, e.g., a publically elected school board
Designs and develops education standards and goals, including curriculum for a specific need or purpose
May be authorized to provide credentials, such as a technical education certificate
Has an organizational structure which could include a superintendent who is either appointed or elected
Has one or more schools that it manages or operates
May provide specialized educational services or related services to other education agencies
Procures and allocates funding from federal, state and local sources for schools and other education and related services
As noted in the table on expected reporting, these districts may not report students in the Membership file (FS 052) if all the students are reported elsewhere.
Service Agency
Some states have LEAs that provide specialized educational and related services to other LEAs. If the state has such entities, then the state submits records on those education units in the LEA level file.
-
Definition from the Previous Clearance – Regional Education Service Agency
A regional education service agency (RESA) is an agency created for the purposes of providing specialized educational services (such as vocational education and other specialized education) or related services (such as services in IEPs) to other education agencies that the agencies cannot readily provide for themselves.
Under the proposed change, the name would be changed to be more generic. Service agencies would provide services but would not operate schools. The box below contains the revised definition of a service agency.
-
Revised! (60), Revised! (30), Final Proposed Definition – Service Agency
A service agency is an agency that does not operate schools instead it provides specialized educational services (such as career and technical education) or related services (such as services in IEPs) to other education agencies that the agencies cannot readily provide for themselves.
The state may use a different name for these entities, such as, regional education service agency (RESA), education service agency (ESA) or board of cooperative education services (BOCES).
State Operated Agencies
Some states have schools that are operated by a state agency. For example, a state may have a state school for the blind. As another example, the state’s Department of Justice may operate the schools in detention or correctional facilities. The SEA submits records at the LEA for the state operated agency so that the schools can be associated with that state operated agency.
-
Definition from Previous Clearance – State Operated Agency
State operated agency is a state agency that provides elementary and/or secondary level instruction.
This definition is being revised to clarify that state operated agencies operate schools and programs.
-
Revised! (60), Revised ! (30) Proposed Definition – State Operated Agency
State operated agency is an organization overseen by a state agency that operates schools or programs that provide public elementary and/or secondary level instruction.
While state operated agencies are submitted by the SEA and in the EDFacts hierarchy under the SEA, this does not mean that those agencies are necessarily under the authority of the SEA.
Federal Operated Agencies
Some states have schools that are operated by a federal agency, e.g., Department of Defense or the Bureau of Indian Education (BIE). SEAs report these schools only when the SEA runs programs in these schools and thus has data to report for these schools. When this occurs, the SEA either associates those schools with a state LEA coordinating the program OR sets up an LEA for the federal agency.
-
Definition from Previous Clearance – Federal Operated Agency
Federal operated agency is a federal agency that provides elementary and/or secondary level instruction.
This definition is being revised to clarify that federal operated agencies operate schools and programs.
-
Revised! (60) Proposed Definition – Federal Operated Agency
Federal operated agency is an organization overseen by a federal agency that operates schools or programs that provide public elementary and/or secondary level instruction.
Independent Charter Districts
See section on “States with Charter Schools” for an explanation of independent charter districts.
School Level
The school level file should contain all the public elementary/secondary schools in the state.
Below is the definition of a public school from the previous clearance.
-
Definition from Previous Clearance – Public School
A public school is an institution that provides educational services and
Has one or more grade groups (PK through 12 grade) or is ungraded,
Has one or more teachers,
Is located in one or more buildings,
Has assigned administrator(s),
Receives public funds as its primary support, and
Is operated by an educational agency.
The term “institution,” as previously used in the definition of school, is being changed because the term often refers to a set or configuration of widely held and relatively deeply imbedded values. Whereas, the term “organization” often refers to an organized set of actions and activities designed to accomplish specific ends.
The definition is being simplified. The characteristics of a school are being removed from the definition. In addition, the name is being clarified by adding “Elementary/Secondary.”
The proposed definition of public elementary/secondary school is in the box below.
Revised! (60), Revised! (30) Proposed Definition – Public Elementary/Secondary School
A public elementary/secondary school is an organization authorized by public authority and financed primarily through public funds to provide public education to students. |
Under this definition, schools:
Are operated by a public school district, independent charter district or state agency on behalf of the state (or federal government in the case of BIE and DoD schools)
Provides instruction for students
Have, will have or had one or more students 2
Have, will have or had one or more teachers
Have an assigned administrator(s) (principal) responsible to public authority
Receive public funds as its primary support
The phrase “have, will have or had” is intended to capture schools that may not have students or teachers at the time the directory is submitted. For example, a school that is being planned and reported as “future” operating status may not currently have students or teachers.
Public elementary/secondary schools are reported by type.
Name |
School type |
|
DG |
21 |
|
Definition |
The classification of schools based on the curriculum concentration. |
|
Permitted Values Final
|
1 - Regular school 2 - Special education school 3 – Career and technical education school 4 - Alternative education school
When needed to report data
5 - Reportable program |
|
Expected reporting by type
Appendix A of this attachment contains a list of files submitted at the school level. The table below indicates the expecting reporting of key date by the type of school.
Data reported |
Regular (1) |
Special Education (2) |
Career and Technical (3) |
Alternative (4) |
CCD |
||||
Membership (FS 052) |
Yes |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Yes |
Staff (FS 059) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
CSPR |
||||
Assessment |
Yes |
Maybe |
Maybe |
Yes |
CRDC |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes1 |
Yes |
FAFSA |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes1 |
Yes |
Notes |
1 If students are at the school more than ½ of the school day. |
|||
For CCD, students are reported at the school level at their school of record. In some states, a special education or career and technical school does not have students in membership to report because all of the students attending the school are shared-time students with a different school of record.
Regular School
Regular schools are public elementary/secondary schools.
-
Definition – Regular School
A regular school is a public elementary/secondary school that does not focus primarily on career and technical, special, or alternative education, although it may provide these programs in addition to a regular curriculum.
Special Education Schools
Special education schools are public elementary/secondary schools.
-
Definition from the Previous Clearance– Special Education School
A special education school is a public elementary/secondary school that focuses primarily on serving the educational needs of students with disabilities (IDEA).
The definition is being revised to match the definition used by CCD.
-
Revised! (30) Definition – Special Education School
A special education school is a public elementary/secondary school that focuses primarily on serving the educational needs of students with disabilities (IDEA) and which adapts curriculum, materials, or instruction for these students.
Career and Technical Education Schools
Career and technical3 education schools are public elementary/secondary schools.
-
Final Definition – Career and Technical Education School
A career and technical education school is a public elementary/secondary school that focuses primarily on providing secondary students with an occupationally relevant or career–related curriculum, including formal preparation for technical or professional occupations.
Alterative Education Schools
Alternative education schools are public elementary/secondary schools.
-
Definition from the Previous Clearance – Alterative Education School
An alternative education school is a public elementary/secondary school that provides nontraditional education; serves as an adjunct to a regular school; and falls outside the categories of regular, special education, or vocational education. It addresses the needs of students that typically cannot be met in a regular, special education or vocational school program.
The definition is being revised to focus on schools that are designed to meet student needs instead of how the needs are meet. Thus the terms “nontraditional” and “adjunct” are removed from the definition. The definition is also being revised to align with the Civil Rights Data Collection (CRDC) by adding that alternative schools are designed to meet the needs of students with academic difficulties and/or discipline problems.
-
Revised! 60, Revised! (30) Proposed Definition - Alterative Education School
An alternative school is a public elementary or secondary school that addresses the needs of students that typically cannot be met in a regular school program and is designed to meet the needs of students with academic difficulties, students with discipline problems, or both students with academic difficulties and discipline problems.
Reportable Program
The permitted value “reportable program” is available for SEAs that have data to report to EDFacts at the school level4 that the SEA has determined does not meet the definition of a public elementary/secondary school provided earlier in this document.
States with Charter Schools
This section describes reporting for states that have legislation for charter schools. The diagram below illustrates the education units and other organizations that can be involved when a state has charter schools.
Charter
Legislation
Regular
Public School District Or Independent
Charter District
Charter
Authorizer
Charter
Charter
School
|
As illustrated in the diagram, the state legislation designates certain entities with the authority to establish charter schools. Every charter school has a charter from an authorizer. Like other public elementary/secondary schools, every charter school operates under a school district. The school district may be a regular public school district or, if allowed by state statute, an independent charter district.
The boxes below contain the definitions of these entities.
-
Definition – Charter School
A charter school is a public school that provides free public elementary and/or secondary education to eligible students under a specific charter executed, pursuant to a state charter school law, by an authorized chartering agency/authority and that is designated by such authority to be a public charter school.
A key point in this definition is that charter schools are public elementary and secondary schools.
All states that have charter schools also have charter authorizers, that is, authorized public chartering agencies.
-
Definition – Authorized Public Chartering Agency
An authorized public chartering agency (aka charter authorizer) is a state educational agency, local educational agency, a specialized charter granting entity or Independent Charter Board, Higher Education Institute, Non-profit entity, state, county or local governmental entity, or other entity that has the authority pursuant to state law to authorize or approve a charter school, and to decide to renew, not renew, or revoke charter contracts.
A key point in this definition is the state legislation dictates which entities can be authorizers.
Some states have charter legislation that creates or allows for independent charter districts. In other states, all charter schools are under regular public school districts. If the state has legislation and has created independent charter districts, then any education units created under that authority are reported as independent charter districts.
-
Definition – Independent Charter District
An independent charter district is an education unit created under the state charter legislation that is not under the administrative control of another local education agency and that operates one or more charter schools – and only charter schools.
In some states, charter schools are established as their own LEA. In these cases, the charter school is reported in the LEA file as an independent charter district and in the school file as a charter school.
Directory reporting requirements for states with charter schools
States with charter schools submit a file with the charter authorizers prior to submitting the school level file with the charter schools. The file with the charter authorizer is explained in the section “Charter Authorizer Roster.”
States with independent charter district include those entities in the LEA level file prior to submitting the school level file with the charter schools.
Summary
This section summarizes the directory file submitted by each state. The diagram below shows the education unit types submitted at each file level. The diagram also illustrates the most common relationships between education units at the LEA level file and education units at the school level file. States can have relationships between education units that are not illustrated in this diagram.
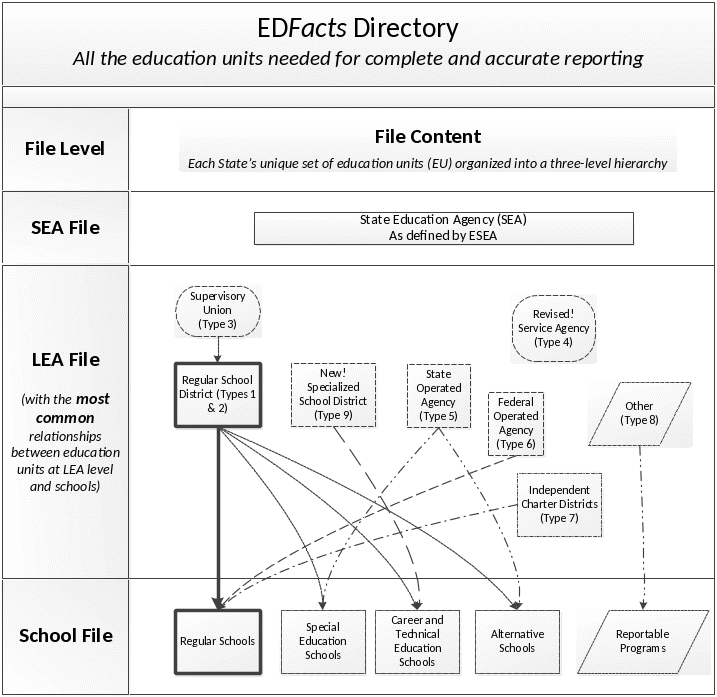
As indicated in the diagram, every state submits a record for the state education agency (SEA) in the SEA file.
Every state submits records for the regular school districts (types 1 or 2). Some states also have supervisory unions, specialized school districts, service agencies, state operated agencies, federal operated agencies, or independent charter districts. Records for supervisory unions are linked to regular school districts (type 2). When necessary, the state uses the type “other” (type 8).
Every state submits regular schools linked to regular school districts. States may also have special education, career and technical education or alternative schools linked to the regular school districts. States with specialized school districts, state operated agencies, federal operated agencies or independent charter districts report the schools belonging to those entities. When necessary, the state uses the type “reportable program.”
Section 2
Data Collected
New! Metadata Collected About the Directory
In addition to the directory files, this package proposes an EMAPS metadata survey to collect information about the directory records submitted so that its state’s directory can be properly interpreted. ED plans to collect this metadata annually. Like other EMAPS surveys, ED plans to have a resubmit period in cases SEAs need to modify their metadata.
SEAs are supposed to report all schools in the state. In some states, some schools are operated, coordinated or supervised by another state agency and the SEA does not have agreements with that agency to share all the necessary data to report these schools in the Directory (FS 029), Membership (FS 052), and/or Staff (FS 059) files. To get understanding of the scope of the files submitted, the following questions about the scope of the directory would be included in the metadata survey. The responses to the questions may trigger additional questions.
Does the school directory file (FS 029) include all schools in the state that provide public elementary and secondary instruction?
Yes
No – This response will trigger additional questions (see below).
(a) Does the LEA membership file (FS 052) include all K-12 students enrolled in the state being provided public elementary and secondary instruction?
Yes
No – This response will trigger additional questions (see below).
(b) Does the school membership file (FS 052) include all K-12 students enrolled in the state being provided public elementary and secondary instruction?
Yes
No – This response will trigger additional questions (see below).
(a) Does the LEA staff file (FS 059) include all staff in the state employed or contracted by LEAs and public schools?
Yes
No – This response will trigger additional questions (see below).
(b) Does the school staff file (FS 059) include all staff in the state employed or contracted by LEAs and public schools?
Yes
No – This response will trigger additional questions (see below).
If an SEA responds “Yes” to all three questions, the SEA is provided with an optional comment box to provide any information about the directory the SEA deems important for ED to know. Following the optional comment box, the survey ends. |
If an SEA responds “No” to one or more of the above questions, then additional questions will be triggered.
Question #1: A “No” response (regarding the school directory file) will trigger the following additional questions:
Are these schools operated or supervised by another state agency?
Yes
No
Which of the following types of schools are not included in the directory? Check all that apply.
Schools that provide special education and related services to children with disabilities under IEPs
Schools that provide career and technical education
Schools that are correctional facilities, detention centers, or treatment centers
Other type of schools
Question #2: A “No” response (regarding the membership file) will trigger the following additional questions:
Which K-12 students are not included in the membership file at the LEA level? Check all that apply.
Students enrolled in schools that provide special education and related services to children with disabilities under IEPs
Students enrolled in schools that provide career and technical education
Students enrolled in schools that are correctional facilities, detention centers, or treatment centers
Students enrolled in other type of schools
Which K-12 students are not included in the membership file at the school level? Check all that apply.
Students enrolled in schools that provide special education and related services to children with disabilities under IEPs
Students enrolled in schools that provide career and technical education
Students enrolled in schools that are correctional facilities, detention centers, or treatment centers
Students enrolled in other type of schools
Question #3: A “No” response (regarding the staff file) will trigger the following additional questions:
Which staff are not included in the staff file at the LEA level? Check all that apply.
Staff working in LEAs or schools that provide special education and related services to children with disabilities under IEPs
Staff working in LEAs or schools that provide career and technical education
Staff working in LEAs or schools that are correctional facilities, detention centers, or treatment centers
Staff working in other type of LEAs or schools
Which teachers are not included in the staff file at the school level? Check all that apply.
Teachers working in schools that provide special education and related services to children with disabilities under IEPs
Teachers working in schools that provide career and technical education
Teachers working in schools that are correctional facilities, detention centers, or treatment centers
Teachers working in other type of schools
After these additional questions, the SEA is provided with an optional comment box to provide any information about the directory the SEA deems important for ED to know. Following the optional comment box, the survey ends. |
For the Directory Of SEAs, LEAs, and Schools
As mentioned in the section “What is the Directory,” the directory data are organized as unique identifiers, contact information and descriptive information. The following table displays which directory data groups are collected from SEAs for each tier in the hierarchy of education units. In the next pages, there is a detailed description of each of these data groups. LEA and school type (DG 453 and 21) were discussed in the section “How the directory is organized.”
By Tier |
1st - SEA |
2nd - LEA |
3rd - School |
DG Name |
DG Name |
DG Name |
|
Unique Identifiers |
559 State code |
559 State code |
559 State code |
7 Education entity name |
7 Education entity name |
7 Education entity name |
|
|
551 Supervisory union ID1 |
|
|
|
4 LEA identifier (State) |
4 LEA identifier (State) |
|
|
|
5 School identifier (State) |
|
|
1 LEA identifier (NCES) |
1 LEA identifier (NCES) |
|
|
|
529 School identifier (NCES) |
|
Contact Information |
9 Address location |
9 Address location |
9 Address location |
8 Address mailing |
8 Address mailing |
8 Address mailing |
|
|
669 Out of state indicator |
669 Out of state indicator |
|
10 Telephone - education entity |
10 Telephone - education entity |
10 Telephone - education entity |
|
11 Web site address |
11 Web site address |
11 Web site address |
|
458 Chief state school officer contact information |
|
|
|
Descriptive Information |
|
16 LEA operational status |
531 School operational status |
|
|
743 Reconstituted status |
|
|
453 LEA type2 |
21 School type |
|
|
18 Grades offered |
18 Grades offered |
|
|
653 Charter status |
27 Charter status |
|
|
|
804 Charter authorizer identifier3 |
|
|
|
|
Unique Identifiers
The table below lists the unique identifiers collected to identify SEAs, LEAs, and school.
DG |
Name |
Definition |
SEA |
LEA |
SCH |
559 |
State code |
The two digit American National Standards Institute (ANSI) code for the state, District of Columbia, and the outlying areas and freely associated areas of the United States. |
X |
X |
X |
7 |
Education entity name |
The full registered name of the school, LEA, SEA, or other entity reporting education data. |
X |
X |
X |
551 |
Supervisory union identification number |
The three-digit unique identifier assigned to the supervisory union. |
|
* |
|
4 |
LEA identifier (state) |
The identifier assigned to an LEA by the SEA. Also known as State LEA Identification Number (ID). |
|
X |
X |
5 |
School identifier (state) |
The identifier assigned to a school by the SEA. Also known as State School Identification Number (ID). |
|
|
X |
1 |
LEA identifier (NCES) |
The seven-digit unique identifier assigned to the LEA by NCES. Also known as NCES LEA ID. |
|
X |
X |
529 |
School identifier (NCES) |
The twelve-digit unique identifier assigned to the school by NCES. Also known as NCES School ID. |
|
|
X |
* The supervisory union identification number (DG 551) is used only by SEAs that have supervisory unions.
Contact Information
The table below lists the data groups collected on addresses and other contact information.
DG |
Name |
Definition |
SEA |
LEA |
SCH |
9 |
Address location |
The set of elements that describes the physical location of the education entity, including the street address, city, state, ZIP Code and ZIP Code + 4. |
X |
X |
X |
8 |
Address mailing |
The set of elements that describes the mailing address of the education entity, including the mailing address, city, state, ZIP Code and ZIP Code + 4. |
X |
X |
X |
669 |
Out of state indicator |
An indication that the mailing or location address of the LEA or school is outside of the state. {Defaults to “not out of state”} |
|
X |
X |
10 |
Telephone – education entity |
The 10-digit telephone number, including the area code, for the education entity. |
X |
X |
X |
11 |
Web site address |
The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) for the unique address of a Web page of an education entity. |
X |
X |
X |
458 |
Chief state school officer contact information |
The contact information of the chief state school officer, including first and last name, official title, phone number and email address. |
X |
|
|
Descriptive Information
This section explains the data collected to describe LEAs and Schools.
Operational status
Each LEA and school has an operational status as of the beginning of the school year. If the operational status changes during the school year, SEA can update it.
The first time an LEA or school is reported with an operational status of “New,” “Added,” or “Future,” NCES assigns the education unit an NCES identifier.
Because LEA and school operational statuses are slightly different, there is a data group for LEA operational status and a data group for school operational status.
LEA
|
|
Name |
LEA operational status |
DG |
16 |
Levels |
LEA |
Definition |
The classification of the operational condition of a local educational agency (LEA). |
The table below explains the operational status for LEAs. The explanations of the statuses have been revised to make them more readable. The table after this table explains which statuses are operational and which are nonoperational.
Status Code |
Status |
This status applies when the LEA: |
1 |
Open |
|
2 |
Closed |
|
3 |
New |
Note:
|
4 |
Added
|
Note:
|
5 |
Changed |
|
6 |
Inactive |
Note
|
7 |
Future |
|
8
|
Reopened |
Note
|
LEAs with an operational statuses report data. LEAs with a non-operational status do not report data. The table below lists the statuses that are operational and non-operational.
-
Operational Statuses
Non-Operational Statuses
1
Open
2
Closed
3
New
6
Inactive
4
Added
7
Future
5
Changed
8
Reopened
School
The operational status of schools is more complicated. In addition to the operational status, for schools, there is a second status: reconstituted status. When a school is reconstituted for purposes of SIG or ESEA accountability provisions, the school may not be recognized as a new school for the purposes of CCD and thus does not receive a new NCES ID. A school is defined as a new school if it is merged with another or undergoes substantial and significant changes. This data group provides a record that an existing school has undergone a school restructuring or transformation when it closes and reopens but does not meet the CCD criteria for being recognized as a new school. This indicator is used in the school year that the school implements the restructuring or transformation change.
|
|
Name |
School operational status |
DG |
531 |
Levels |
School |
Definition |
The classification of the operational condition of a school. |
The table below explains the operational status for schools. The explanations of the statuses have been revised to make them more readable. The table after this table explains which statuses are operational and which are nonoperational.
Status Code |
Status |
This status applies when the school: |
1 |
Open |
|
2 |
Closed |
|
3 |
New |
Notes:
|
4 |
Added |
Note:
|
5
|
Changed LEA affiliation |
|
6 |
Inactive |
Note
|
7 |
Future |
|
8
|
Reopened |
Note
|
Schools with an operational statuses report data. Schools with a non-operational status do not report data. The table below lists the statuses that are operational and non-operational.
-
Operational Statuses
Non-Operational Statuses
1
Open
2
Closed
3
New
6
Inactive
4
Added
7
Future
5
Changed LEA affiliation
8
Reopened
In addition to operational status, SEAs report school reconstituted status.
|
|
Name |
Reconstituted status |
DG |
743 |
Levels |
SCH |
Definition |
The school was restructured, transformed or otherwise changed as a consequence of the state’s accountability system under ESEA or as a result of School Improvement Grants (SIG), but is not recognized as a new school for CCD purposes. |
Permitted Values |
|
Grades
SEAs submit data on which grades are offered by the LEAs and schools.4
ED derives grades provided based on the membership data submitted. If student counts are submitted for a grade, then that grade is assumed to be provided.
|
||
Name |
Grades offered |
|
DG |
18 |
|
Levels |
LEA, SCH |
|
Definition |
The grade level(s) offered by the school or district. |
|
Permitted Values |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charters
Some states have specific legislation allowing charter schools.
|
|
Name |
Charter status |
DG |
27 |
Levels |
SCH |
Definition Revised! (60) |
An indication that a public school provides free public elementary and/or secondary education to eligible students under a specific charter executed, pursuant to a state charter school law, by an authorized chartering agency/authority and that is designated by such authority to be a public charter school. |
Permitted Values
|
|
Each charter school has an authorizer. Schools with the charter status (DG 27) equal to “yes” also report their charter authorizer using the identifier that links to the charter authorizer roster.
|
|
Name |
Charter authorizer identifier (state) |
DG |
804 |
Levels |
SCH |
Definition |
The identifier assigned to an authorized public chartering agency by the SEA. |
In some states the legislation for charter schools provides the charter school with authority similar to school districts. In other states, charter schools are always under the authority of another LEA, usually an existing school district.
Whenever, an LEA is reported with an LEA type of “independent charter district,” the SEA also reports the type of authority that the education unit has related to U.S. Department of Education programs.
|
|
Name |
Charter LEA status |
DG ID |
27 |
Levels |
LEA |
Definition |
The status of a charter district as an LEA for purposes of federal programs. |
Permitted Values
|
|
Virtual
Virtual school status (DG 803) will be moved to CCD School File (FS 129).
Other descriptive information
Outside the directory files, other descriptive information is submitted, for example, Title I school status, shared school status, and magnet status. These data groups are described in the Attachment on Data Groups (Attachment B-3).
Charter Authorizer Roster
To ensure completeness of data on charter schools, SEAs submit a file (FS 190) with the list or roster of authorized public chartering agencies (aka charter authorizers) in their state. The charter schools are linked to the charter authorizers using the identifier. Only states that have charter schools submit data on charter authorizers.
Detailed Description of the Roster
Below are detailed descriptions of data groups used for the roster of charter authorizers. Similar to other education entities, the data groups are organized as unique identifiers, contact information and descriptive information.
Unique identifiers
The unique identifiers for charter authorizers are the name, state code and a state identifier.
DG |
Name |
Definition |
798 |
Charter authorizer name |
The full legally accepted name of the authorized public chartering agency that currently oversees the charter school. |
559 |
State code |
The two digit American National Standards Institute (ANSI) code for the state, District of Columbia, and the possessions (outlying areas) and freely associated areas of the United States. |
808 |
Charter authorizer identifier (state) |
The unique identifier assigned to an authorized public chartering agency by the SEA. |
Contact information
The roster includes the standard contact information of mailing and location address.
DG |
Name |
Definition |
805 |
Charter authorizer address location |
The set of elements that describes the physical location of the authorized public chartering agency, including the street address, city, state, ZIP Code and ZIP Code + 4. |
806 |
Charter authorizer address mailing |
The set of elements that describes the mailing address of the authorized public chartering agency, including the mailing address, city, state, ZIP Code and ZIP Code + 4. |
Descriptive information
The roster includes information about the type of organization that the charter authorizer is.
|
|
Name |
Charter authorizer type |
DG |
809 |
Definition |
The type of organization |
Permitted Values
|
|
Linking Charter Schools to Charter Authorizers
Charter schools are linked to the charter authorizers using the charter authorizer identifier. The identifiers associated with the charter authorizers are collected and reported in the aforementioned charter authorizer roster. The identifiers associated with the charter school are also reported in the school level directory for any school with a “yes” for charter status (DG 27).
New! Charter Management Organizations roster
The data requirements for the charter management organizations roster were moved to Attachment B-3.
Appendix A – Definition of LEA from CFR
Below is the definition of an LEA from the Code of Federal Regulations.
§ 303.23 Local educational agency
(a) General. Local educational agency or LEA means a public board of education or other public authority legally constituted within a State for either administrative control or direction of, or to perform a service function for, public elementary schools or secondary schools in a city, county, township, school district, or other political subdivision of a State, or for a combination of school districts or counties as are recognized in a State as an administrative agency for its public elementary schools or secondary schools.
(b) Educational service agencies and other public institutions or agencies. The term includes the following:
(1) Educational service agency, defined as a regional public multiservice agency—
(i) Authorized by State law to develop, manage, and provide services or programs to LEAs; and
(ii) Recognized as an administrative agency for purposes of the provision of special education and related services provided within public elementary schools and secondary schools of the State.
(2) Any other public institution or agency having administrative control and direction of a public elementary school or secondary school, including a public charter school that is established as an LEA under State law.
(3) Entities that meet the definition of intermediate educational unit or IEU in section 602(23) of the Act, as in effect prior to June 4, 1997. Under that definition an intermediate educational unit or IEU means any public authority other than an LEA that—
(i) Is under the general supervision of a State educational agency;
(ii) Is established by State law for the purpose of providing FAPE on a regional basis; and
(iii) Provides special education and related services to children with disabilities within the State.
(c) BIE-funded schools. The term includes an elementary school or secondary school funded by the Bureau of Indian Education, and not subject to the jurisdiction of any SEA other than the Bureau of Indian Education, but only to the extent that the inclusion makes the school eligible for programs for which specific eligibility is not provided to the school in another provision of law and the school does not have a student population that is smaller than the student population of the LEA receiving assistance under the Act with the smallest student population.
(Authority: 20 U.S.C. 1401(5), 1401(19))
Appendix B - Files Submitted at the School Level
Below is a list of files submitted at the school level. SEAs should include in the school level file all education units (using reportable program, if necessary) to completely and accurate report these files.
File Specification Number |
File Specification Name |
Scope limitations |
002 |
Children with Disabilities (IDEA) School Age |
|
030 |
Discipline Incidents |
|
032 |
Dropouts |
|
033 |
Free and Reduced Price Lunch |
|
040 |
Graduates/Completers |
Only if has graduation grade levels |
052 |
Membership |
|
059 |
Staff FTE |
|
063 |
Teacher Quality in Elementary Classes |
|
064 |
Teacher Quality in Core Secondary Classes |
|
103 |
Accountability |
|
106 |
Elementary/Middle Additional Indicator |
|
107 |
High School Graduation Rate Indicator |
Only if has High School grade levels |
108 |
Mathematics Participation Status |
|
109 |
AMO Mathematics Status |
|
110 |
Reading/Language Arts Participation Status |
|
111 |
AMO Reading/Language Arts Status |
|
129 |
CCD School |
|
130 |
ESEA Status |
|
132 |
School End of SY Status |
|
139 |
LEP English Language Proficiency Results |
|
150 |
Regulatory Adjusted-Cohort Graduation Rate |
Only if has graduation grade levels |
151 |
Cohorts for Regulatory Adjusted-Cohort Graduation Rate |
Only if has graduation grade levels |
159 |
Average Scale Scores |
|
160 |
High School Graduates Postsecondary Enrollment |
Only if has graduation grade levels |
161 |
High School Graduates Postsecondary Credits Earned |
Only if has graduation grade levels |
163 |
Discipline Data |
|
165 |
Migrant Data |
|
166 |
Evaluation of Staff |
|
167 |
School Improvement Grants |
Only if SIG school |
171 |
Academic Achievement - Flexibility Subgroups |
Only if SEA has flexibility subgroups |
172 |
Assessment Participation - Flexibility Subgroups |
Only if SEA has flexibility subgroups |
173 |
Status - Flexibility Subgroups |
Only if SEA has flexibility subgroups |
174 |
Graduation Rates - Flexibility Subgroups |
Only if SEA has flexibility subgroups |
175 |
Academic Achievement in Mathematics |
|
176 |
State Interventions – Flexibility |
Only if SEA has flexibility |
177 |
Graduation Cohorts - Flexibility Subgroups |
Only if SEA has flexibility subgroups |
178 |
Academic Achievement in Reading/Language Arts |
|
179 |
Academic Achievement in Science |
|
183 |
Title I Allocations – Flexibility |
Only if SEA has flexibility |
185 |
Assessment Participation in Mathematics |
|
188 |
Assessment Participation in Reading/Language Arts |
|
189 |
Assessment Participation in Science |
|
Appendix C - Data Derived
This appendix describes some of the data that are derived and added to the directories of LEAs and schools. This material had been included in the explanation of the directory data in previous clearances.
Title I
For the Consolidated State Performance Report and other data uses, LEAs that are Title I districts need to be identified.
|
|
Name |
Title I district status |
DG ID |
582 |
Definition |
The district is designated under state and federal regulations as receiving Title I funds. |
Level |
LEA |
How obtained |
OESE provides a list of the districts designated as Title I districts. |
Geographic data
The data on geographic location, locale code and association with counties and Congressional districts also have many uses.
|
|
Name |
Geographic location |
DG |
14 |
Definition |
The latitude and longitude where the education entity is physically located. |
Level |
LEA, SCH |
How obtained |
Census based on location address. |
|
|
|
Name |
County code |
County name |
DG |
12 |
572 |
Definition |
The County code of the county, parish, borough, or comparable unit (within a state) in which an address is located. |
The name of a county, parish, borough, or comparable unit (within a state) in which an education unit is located. |
Level |
LEA, SCH |
|
How obtained |
Census based on location address. |
|
|
|
Name |
Congressional district number |
DG |
13 |
Definition |
The legally accepted number of an area established by law for the election of representatives to the United States Congress where the school or district is located. |
Level |
LEA, SCH |
How obtained |
Census based on location address. |
|
||
Name |
Locale |
|
DG |
17 |
|
Definition |
The designation of a school's or district's degree of urbanization based on its geographic location and population attributes such as density. May also be known as “urbanicity.” |
|
Level |
LEA, SCH |
|
How obtained |
Census based on location address. |
|
Permitted Values assigned by Census |
City, Large
|
Territory inside an urbanized area and inside a principal city with population of 250,000 or more. |
City, Midsize
|
Territory inside an urbanized area and inside a principal city with population less than 250,000 and greater than or equal to 100,000. |
|
City, Small
|
Territory inside an urbanized area and inside a principal city with population less than 100,000. |
|
Suburb, Large
|
Territory outside a principal city and inside an urbanized area with population of 250,000 or more. |
|
Suburb, Midsize |
Territory outside a principal city and inside an urbanized area with population less than 250,000 and greater than or equal to 100,000. |
|
Suburb, Small |
Territory outside a principal city and inside an urbanized area with population less than 100,000. |
|
Town, Fringe: |
Territory inside an urban cluster that is less than or equal to 10 miles from an urbanized area. |
|
Town, Distant: |
Territory inside an urban cluster that is more than 10 miles and less than or equal to 35 miles from an urbanized area. |
|
Town, Remote: |
Territory inside an urban cluster that is more than 35 miles from an urbanized area. |
|
Rural, Fringe |
Census-defined rural territory that is less than or equal to 5 miles from an urbanized area, as well as rural territory that is less than or equal to 2.5 miles from an urban cluster. |
|
Rural, Distant |
Census-defined rural territory that is more than 5 miles but less than or equal to 25 miles from an urbanized area, as well as rural territory that is more than 2.5 miles but less than or equal to 10 miles from an urban cluster. |
|
Rural, Remote |
Census-defined rural territory that is more than 25 miles from an urbanized area and is also more than 10 miles from an urban cluster |
|
Census Classifications
Every five years, Census collects data about state and local governments. The data in the Census of Governments is used for the collection of fiscal data on public education through the F-33.
LEA level
Census matches the education units submitted in the LEA level file to the census of governments. The education units in that file are classified as:
Independent school districts – A public school district that is independent of other government agencies, such as having the authority to collect taxes.
Dependent school districts – A public school district that is within another government agency, such as a county, city, that is, dependent for funding on that city, county entity, regardless of the scope of the LEA’s authority with respect to the management of education
Other education activity – An education unit that performs activities related to education but, do not operate schools.
Census then assigns a government identification number to education units in the LEA file that are independent governments. Education units classified as dependent school districts or other education activity are not assigned government identification numbers.
School level
Census also adds a classification to the education units in the school file. That classification labels each school by education level.
|
|
Name |
School level |
DG |
TBD |
Definition |
The classification of a school by education level. |
Level |
SCH |
Permitted Values |
|
How obtained |
By grades offered |
Financial
The U.S. Department of Education distributes grant money through G5 using DUNS numbers as a unique identifier. To link grants to education units in EDFacts, the DUNS numbers must be linked to the state or NCES ID numbers.
|
|
Name |
DUNS number |
DG ID |
6 |
Definition |
DUNS (Data Universal Numbering System) is the unique nine-digit identification number assigned to a business entity by Dunn and Bradstreet. |
Level |
SEA, LEA |
How obtained |
Mapping |
1 Previously, the terms “education agency” or “educational agency” were used, the proposal is to discontinue using both terms that are too generalized a conception of any agency that acts on behalf of education. Instead, the term “local education agency” would be used. When the term education agency is used, it will pertain only in the general sense to focus on the function of an agency (i.e., education), not the level at which it functions.
1 The educational credential includes both the authorization to proceed to the next grade level and the high school diploma.
2A school may not have membership to report. Students could be attending the school part time.
3 Career and technical schools were referred to previously as vocational schools.
4 Appendix B lists the files submitted at the school level.
1 Supervisory union ID or identification number (DG 551) is used only by states that have supervisory unions.
2 Previously named “education agency type”
3 Charter authorizer identifier (DG 804) is reported only if the school is a charter school, that is, charter status (DG 27) equals “yes.” See the section on the charter authorizer roster for more information.
4 If SEAs submit data using XML, the directory and grades offered are in the same file: X029. If SEAs submit data using fixed or delimited files, the directory and grades offered are in different files: N029 for the directory data and N039 for the grades offered data.
| File Type | application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document |
| File Title | Attachment B-2 Directory |
| Author | bethyoung@qi-partners.com |
| File Modified | 0000-00-00 |
| File Created | 2021-05-24 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy