CMS-10219 CMS-10219.3_Effectiveness of Care B_pp 112-178
HEDIS Information Collection Request
CMS-10219.3_Effectiveness of Care B_pp 112-178
HEDIS Information Collection Request
OMB: 0938-1028
Effectiveness
of Care: Comprehensive Diabetes Care
Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added HbA1c good control (<7.0%) as a first year indicator.
Restricted LDL-C screening and control criteria to require testing during the measurement year.
Retired LDL-C control <130 mg/dL.
Clarified requirements for the medical attention for nephropathy indicator.
Added use of ACE inhibitors/ARBs as numerator compliant for medical attention for nephropathy.
Added blood pressure control <130/80 mm Hg and <140/90 mm Hg as first year indicators.
Changed 70/30 to Mix 70/30 in Table CDC-A.
Added ActosPlus Met, Apidra, Avandamet, Avandaryl, Byetta, Exubera, Lantus, Levemir, Metaglip,
Mix 50/50, Mix 75/25 to Table CDC-A.Separated diagnosis and visit type codes into two tables (CDC-B, CDC-C).
Added CPT codes 99304–99310, 99315, 99316, 99318, 99324–99328, 99334–99337, 99455, 99456 to Table CDC-C.
Deleted CPT codes 99271–99275, 99292, 99351–99357 from Table CDC-C.
Deleted UB-92 Revenue codes 0115, 0125, 0135, 0145, 0155, 049x, 050x, 053x, 056x, 065x, 076x, 092x, 094x, 096x, 0972–0979, 0984–0986, 0988, 0989 from Table CDC-C.
Moved UB-92 Revenue code 0456 from outpatient/nonacute inpatient description to emergency department description in Table CDC-C.
Added CPT code 83037 to Table CDC-D.
Added CPT Category II codes to Tables CDC-D, CDC-F, CDC-G, CDC-I, CDC-J.
Deleted LOINC code 17855-8 from Table CDC-D.
Added Table CDC-E: Codes to Identify HbA1c Levels.
Added CPT codes 67028, 67038-67040 to Table CDC-F.
Deleted CPT code 92287 from Table CDC-F.
Added HCPCS codes to Tables CDC-F, CDC-J.
Deleted ICD-9-CM Diagnosis code V72.0 from Table CDC-F.
Added CPT codes 83700, 83701, 83704 to Table CDC-G.
Added LOINC code 39469-2 to Table CDC-G.
Added Table CDC-H: Codes to Identify LDL-C Levels.
Deleted CPT codes 83518, 84160, 84165, 84166, 81050 from Table CDC-I.
Added CPT codes 36145, 36831-36833, 90939, 90940 codes to Table CDC-J.
Added ICD-9-CM Diagnosis code 791.0 to Table CDC-J.
Added ICD-9-CM Procedure code 38.95 to Table CDC-J.
Added UB-92 Revenue code 0367 to Table CDC-J.
Added exclusion criteria for members with gestational diabetes and steroid-induced diabetes.
Description
The percentage of members 18–75 years of age with diabetes (type 1 and type 2) who had each of the following.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing
HbA1c poor control (>9.0%)
HbA1c good control (<7.0%)
Eye exam (retinal) performed
LDL-C screening performed
LDL-C control (<100 mg/dL)
Medical attention for nephropathy
Blood pressure control (<140/90 mm Hg)
Blood pressure control (<130/80 mm Hg)
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
18–75 years as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during the measurement year. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage (i.e., a member whose coverage lapses for 2 months [60 days] is not considered continuously enrolled). |
Anchor date |
December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefit |
Medical. |
Event/diagnosis |
Two methods identify diabetic members.
The MCO must use both methods to identify the eligible population; however, to be included in the measure, a member needs to be identified in only one method. Members may be identified as having diabetes during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. Pharmacy data. Members who were dispensed insulin or oral hypoglycemics/ antihyperglycemics during the measurement year or year prior to the measurement year on an ambulatory basis (Table CDC-A). |
Table CDC-A: Prescriptions to Identify Diabetics
Description |
Prescriptions |
|||
Insulin |
|
|
|
|
Oral hypoglycemic/ antihyperglycemic |
|
|
|
|
Note: Removed Glucophage/metformin from Table CDC-A in HEDIS 2005. Diabetic members on these medications are identified through diagnosis coding only. NCQA’s Web site at www.ncqa.org will provide a list of medications by November 15, 2006.
Claim/encounter data. Members who had two face-to-face encounters with different dates of service in an outpatient setting or nonacute inpatient setting or one face-to-face encounter in an acute inpatient or emergency department (ED) setting during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year with a diagnosis of diabetes. The MCO may count services that occur over both years. Use the codes in Table CDC-B to identify a diabetes diagnosis and Table CDC-C to identify the visit type.
Table CDC-B: Codes to Identify Diabetes
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
DRG |
Diabetes |
250, 357.2, 362.0, 366.41, 648.0 |
294, 295 |
Table CDC-C: Codes to Identify Visit Type
Description |
CPT |
UB-92 Revenue |
Outpatient |
92002-92014, 99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99217-99220, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99384-99387, 99394-99397, 99401-99404, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429, 99455, 99456, 99499 |
051x, 052x, 057x-059x, 077x, 082x-085x, 088x, 0982, 0983 |
Nonacute inpatient |
99301-99313, 99315, 99316, 99318, 99321-99328, 99331-99337 |
0118, 0128, 0138, 0148, 0158, 019x, 055x, 066x |
Acute inpatient |
99221-99223, 99231-99233, 99238, 99239, 99251-99255, 99261-99263, 99291 |
010x, 0110-0114, 0119, 0120-0124, 0129, 0130-0134, 0139, 0140-0144, 0149, 0150-0154, 0159, 016x, 020x-022x, 072x, 080x, 0987 |
Emergency department |
99281-99285 |
045x, 0981 |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerators |
|
HbA1c testing |
An HbA1c test performed during the measurement year, as identified by claim/ encounter or automated laboratory data. Use any code listed in Table CDC-D. |
Table CDC-D: Codes to Identify HbA1c Tests
CPT |
CPT Category II |
LOINC |
83036, 83037 |
3046F, 3047F |
4548-4, 4549-2, 17856-6 |
Poor HbA1c control |
Using automated laboratory data, identify the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year. The member is numerator compliant if the most recent automated HbA1c level is >9.0% or is missing a result or if an HbA1c test was not done during the measurement year. The member is not numerator compliant if the automated result for the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year is ≤9.0%. If the most recent test during the measurement year is identified by a CPT Category II code, use Table CDC-E to evaluate whether the member is numerator compliant (3046F indicates the member is numerator compliant; 3047F indicates the member is not numerator compliant). Note: For this indicator, a lower rate indicates better performance (i.e., low rates of poor control indicate better care). |
Table CDC-E: Codes to Identify HbA1c Levels
Description |
CPT Category II |
Numerator compliant (HbA1c >9.0%) |
3046F |
Not numerator compliant (HbA1c ≤9.0%) |
3047F |
Good HbA1c control |
Using automated laboratory data, identify the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year. The member is numerator compliant if the most recent automated HbA1c level is <7.0%. The member is not numerator compliant if the automated result for the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year is ≥7.0% or is missing a result, or if an HbA1c test was not during the measurement year. |
Eye exam |
An eye screening for diabetic retinal disease as identified by administrative data. This includes diabetics who had one of the following.
Use codes listed in Table CDC-F to identify eye exams. For exams performed in the year prior to the measurement year, an automated result must be available. |
Table CDC-F: Codes to Identify Eye Exams*
CPT |
CPT Category II** |
HCPCS |
ICD-9-CM Procedure |
67028, 67038-67040, 67101, 67105, 67107, 67108, 67110, 67112, 67141, 67145, 67208, 67210, 67218, 67227, 67228, 92002, 92004, 92012, 92014, 92018, 92019, 92225, 92226, 92230, 92235, 92240, 92250, 92260, 99203-99205, 99213-99215, 99242-99245 |
2022F, 2024F, 2026F, 3072F |
S0625, S3000 |
14.1-14.5, 14.9, 95.02-95.04, 95.11, 95.12, 95.16 |
* Eye exams provided by eye care professionals are a proxy for dilated eye examinations because there is no administrative way to determine that a dilated exam was performed.
** The MCO does not need to limit CPT Category II codes to an optometrist or an ophthalmologist because the codes can be used by other provider types to document services provided by an optometrist or ophthalmologist.
LDL-C screening |
An LDL-C test performed during the measurement year, as identified by claim/ encounter or automated laboratory data. Use any code listed in table CDC-G. |
Table CDC-G: Codes to Identify LDL-C Screening
CPT |
CPT Category II |
LOINC |
80061, 83700, 83701, 83704, 83715, 83716, 83721 |
3048F, 3049F, 3050F |
2089-1, 12773-8, 13457-7, 18261-8, 18262-6, 22748-8, 24331-1, 39469-2 |
LDL-C
level |
Using
automated laboratory data, identify the most recent LDL-C
test during If the most recent test during the measurement year is identified by a CPT Category II code, use Table CDC-H to evaluate whether the member is numerator compliant (3048F indicates the member is numerator compliant; 3049F, 3050F indicate the member is not numerator compliant). |
Table CDC-H: Codes to Identify LDL-C Levels
Description |
CPT Category II |
Numerator compliant (LDL-C <100 mg/dL) |
3048F |
Not numerator compliant (LDL-C ≥100 mg/dL) |
3049F, 3050F |
Medical attention for nephropathy |
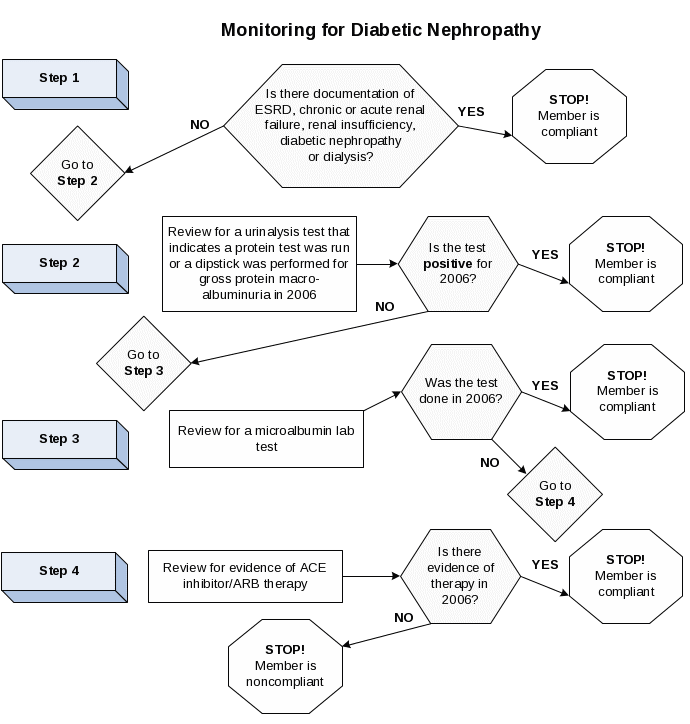
A nephropathy screening test or evidence of nephropathy, as documented through administrative data. Note: A process flow diagram is included at the end of this specification to help implement this specification. |
Nephropathy screening test |
A nephropathy screening test during the measurement year (Table CDC-I). |
Table CDC-I: Codes to Identify Nephropathy Screening Tests
Description |
CPT |
CPT Category II |
LOINC |
Nephropathy screening test |
82042, 82043, 82044, 84156 |
3060F, 3061F |
11218-5, 14956-7, 14957-5, 14958-3, 14959-1, 30000-4, 30001-2, 30003-8, 1753-3, 1754-1, 1755-8, 9318-7, 13705-9, 14585-4, 20621-9, 21059-1, 32294-1, 2887-8, 2888-6, 2889-4, 2890-2, 12842-1, 13801-6, 18373-1, 21482-5, 26801-1, 27298-9, 32209-9, 32551-4, 34366-5, 35663-4 |
Evidence of nephropathy |
Any of the following meet criteria for evidence of nephropathy.
|
Table CDC-J: Codes to Identify Evidence of Nephropathy
Description |
CPT |
CPT Category II |
HCPCS |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
ICD-9-CM Procedure |
UB-92 Revenue |
DRG |
LOINC |
Urine macro-albumin test* |
81000-81003, 81005 |
3062F |
|
|
|
|
|
5804-0, 20454-5, 24356-8, 24357-6 |
Evidence of treatment for nephropathy |
36145, 36800, 36810, 36815, 36818, 36819-36821, 36831-36833, 50300, 50320, 50340, 50360, 50365, 50370, 50380, 90920, 90921, 90924, 90925, 90935, 90937, 90939, 90940, 90945, 90947, 90989, 90993, 90997, 90999, 99512 |
3066F |
G0257, G0314-G0319, G0322, G0323, G0326, G0327, S9339 |
250.4, 403, 404, 405.01, 405.11, 405.91, 581.81, 582.9, 583.81, 584-586, 588, 753.0, 753.1, 791.0, V42.0, V45.1, V56 |
38.95, 39.27, 39.42, 39.43, 39.53, 39.93-39.95, 54.98, 55.4-55.6 |
0367, 080x, 082x-085x, 088x |
316, 317 |
|
ACE inhibitor/ARB therapy |
|
4009F |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* A CPT Category II code indicates a positive result for urine macroalbumin; the MCO must use automated laboratory data to confirm a positive result for tests identified by CPT or LOINC codes.
Table CDC-K: ACE Inhibitors/ARBs
Description |
Drugs |
||||
ACE inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
|
ACE inhibitors—Combination products |
|
|
|||
ARBs |
|
|
|
||
ARB—Combination products |
|
|
|
||
Note: NCQA will provide a comprehensive list of NDC codes on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Blood pressure level <130/80 mm Hg |
Identify the most recent BP during the measurement year. Identify the lowest systolic and lowest diastolic BP reading from the most recent BP notation in the medical record. If there are multiple BPs recorded for a single date, use the lowest systolic and lowest diastolic BP on that date as the representative BP. The member is numerator compliant if the most recent reading is <130/80 mm Hg. If the reading for the most recent BP is ≥130/80 mm Hg or is missing, or if a BP reading was not taken during the measurement year, the member is not compliant. |
Blood pressure level <140/90 mm Hg |
Identify the most recent BP reading during the measurement year. Identify the lowest systolic and lowest diastolic BP reading from the most recent BP notation in the medical record. If there are multiple BPs recorded for a single date, use the lowest systolic and lowest diastolic BP on that date as the representative BP. The member is numerator compliant if the most recent reading is <140/90 mm Hg. If the result for the most recent BP test is ≥140/90 mm Hg or is missing, or if a BP test was not done during the measurement year, the member is not compliant. An MCO that uses CPT Category II codes to identify numerator compliance for this indicator must search for all codes in Table CDC-L and use the most recent codes to evaluate whether the member is numerator compliant. |
Table CDC-L: Codes to Identify Systolic and Diastolic BP Levels
Description |
CPT Category II |
Numerator compliant (BP <140/90 mm Hg) |
3076F with (3078F or 3079F) |
Not numerator compliant (BP ≥140/90 mm Hg) |
3077F, 3080F |
Hybrid Specification
Denominator |
A systematic sample drawn from the eligible population for each product line. |
||
Numerators |
|
||
HbA1c testing |
An HbA1c test performed during the measurement year as identified by administrative data or medical record review. |
||
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
||
Medical record |
At a minimum, documentation in the medical record must include a note indicating the date on which the HbA1c test was performed and the result. The MCO may count notation of the following in the medical record. |
||
|
|
|
|
Poor HbA1c control |
The most recent HbA1c level (performed during the measurement year) is >9.0% or is missing or was not done during the measurement year, as documented through automated laboratory data or medical record review. The member is not numerator compliant if the result for the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year is ≤9.0%. |
||
Note: For this indicator, a lower rate indicates better performance (i.e., low rates of poor control indicate better care).
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
At a minimum, documentation in medical record must include a note indicating the date on which the HbA1c test was performed and the result. |
Good HbA1c control |
The most recent HbA1c level (performed during the measurement year) is <7.0% as identified by automated laboratory data or medical record review. The member is not numerator compliant if the result for the most recent HbA1c test during the measurement year is ≥7.0%, is missing or was not performed during the measurement year. |
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
At a minimum, documentation in medical record must include a note indicating the date on which the HbA1c test was performed and the result. |
Eye exam |
An eye screening for diabetic retinal disease as identified by administrative data or medical record review. This includes diabetics who had one of the following.
|
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
Documentation in the medical record of a retinal eye exam during the measurement year or a negative retinal eye exam during the year prior to the measurement year. At a minimum, documentation in the medical record must include:
|
LDL-C screening |
An LDL-C test performed during the measurement year as identified by claim/ encounter or automated laboratory data or medical record review. Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
|
At a minimum, documentation in the medical record must include a note indicating the date on which the LDL-C test was performed and the result. |
LDL-C
level |
The most recent LDL-C level performed during the measurement year is <100 mg/dL, as documented through automated laboratory data or medical record review. If the result for the most recent LDL-C test during the measurement year is ≥100 mg/dL or is missing, or if an LDL-C test was not done during the measurement year, the member is not numerator compliant. |
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
Documentation in medical record must include, at a minimum, a note indicating the date on which the LDL-C test was performed and the result. The MCO may calculate LDL-C levels from total cholesterol, HDL-C and triglycerides using the Friedewald equation if the triglycerides are ≤400 mg/dL. (LDL-C) = (total cholesterol) – (HDL) – (triglycerides/5) If lipoprotein (a) is measured, this calculation is: (LDL-C) = (total cholesterol) – (HDL) – (triglycerides/5) – 0.3 [lipoprotein (a)] These formulae are used when all levels are expressed in mg/dL and cannot be used if triglycerides >400 mg/dL. |
Medical attention for diabetic nephropathy |
A nephropathy screening test or evidence of nephropathy as documented through either administrative data or medical record review. |
Note: A process flow diagram is included at the end of this specification to help implement this specification.
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
Nephropathy screening test. At a minimum, documentation in medical record must include a note indicating the date on which a urine microalbumin test was performed, and the result. The MCO may count notation of the following in the medical record for urine microalbumin test.
Evidence of nephropathy. Any of the following meet criteria for evidence of nephropathy.
|
|
Note: “Trace” urine macroalbumin test results are not considered numerator compliant.
|
Blood pressure level <130/80 mm Hg |
A BP <130/80 mm Hg as documented through medical record review. |
Blood pressure level <140/90 mm Hg |
A BP <140/90 mm Hg as documented through medical record review. |
Administrative |
Refer to the Administrative Specification above to identify positive numerator hits from administrative data. |
Medical record |
To determine if a member’s BP is adequately controlled, the MCO must identify the representative BP. The MCO should follow the steps below to determine representative BP. |
Step 1 |
|
Step 2 |
|
Exclusions (optional)
Exclude members with a diagnosis of polycystic ovaries who did not have any face-to-face encounters with the diagnosis of diabetes, in any setting, during the measurement year or year prior to the measurement year. Diagnosis of polycystic ovaries can occur at any time in the member’s history, but must have occurred by December 31 of the measurement year. Use the codes in Table CDC-B to identify a diagnosis of diabetes and the codes in CDC-M to identify a diagnosis of polycystic ovaries.
Exclude members with gestational diabetes or steroid-induced diabetes, who did not have any face-to-face encounters with the diagnosis of diabetes (in any setting), during the measurement year or year prior to the measurement year. Diagnosis of gestational diabetes or steroid-induced diabetes can occur during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year, but must have occurred by December 31 of the measurement year. Use the codes in Table CDC-B to identify a diagnosis of diabetes and the codes in CDC-M to identify gestational diabetes and steroid-induced diabetes.
Table CDC-M: Codes to Identify Exclusions
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Polycystic ovaries |
256.4 |
Steroid induced |
251.8, 962.0 |
Gestational diabetes |
648.8 |
Note
The MCO may select data collection methodology (Administrative vs. Hybrid) at the indicator level; however, the methodology for screening and control rates must be consistent.
Many MCOs find a high rate of false positives when they use laboratory data to identify diabetics because diabetes diagnosis codes frequently are reported on laboratory tests used to rule out diabetes; therefore, laboratory data may not be used to identify diabetics. Using the codes provided in the scope of this measure ensures that laboratory data is not used to identify diabetics.
Blindness is not an exclusion for a diabetic eye exam due to the difficulty of distinguishing between individuals who are legally blind but who require a retinal exam and those who are completely blind and therefore do not require an exam.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table CDC-1/2/3: Data Elements for Comprehensive Diabetes Care
|
Administrative |
Hybrid |
Measurement year |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Data collection methodology (administrative or hybrid) |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Eligible population |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of numerator events by administrative data in eligible population (before exclusions) |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Current year’s administrative rate (before exclusions) |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Minimum required sample size (MRSS) or other sample size |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Oversampling rate |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Final sample size (FSS) |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of numerator events by administrative data in FSS |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Administrative rate on FSS |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of original sample records excluded because of valid data errors |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of administrative data records excluded |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of medical record data records excluded |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Number of employee/dependent medical records excluded |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Records added from the oversample list |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Denominator |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Numerator events by administrative data |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Numerator events by medical records |
|
Each of the 9 rates |
Reported rate |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 9 rates |
Each of the 9 rates |
Use of Appropriate Medications for People With Asthma (ASM)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added Table ASM-A: Codes to Identify Asthma.
Added CPT codes 99341–99345, 99347–99350, 99382–99386, 99392–99396, 99401–99404, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429, 99499 to Table ASM-B.
Deleted CPT codes 99271–99275, 99292, 99356, 99537 from Table ASM-B.
Moved UB-92 Revenue code 0456 from outpatient description to emergency department description in Table ASM-B.
Added UB-92 Revenue codes 0511–0514, 0522, 0529, 057x–059x, 0771 to Table ASM-B.
Deleted UB-92 Revenue codes 0115, 0125, 0135, 0145, 0155, 076x, 0988 from Table ASM-B.
Description
The percentage of members 5–56 years of age during the measurement year who were identified as having persistent asthma and who were appropriately prescribed medication during the measurement year.
Definitions
Dispensing event |
A dispensing event is one prescription of an amount lasting 30 days or less. To calculate dispensing events for prescriptions longer than 30 days, divide the days supply by 30 and round down to convert. For example, a 100-day prescription is equal to three dispensing events (100/30 = 3.33, rounded down to 3). In addition, two different prescriptions dispensed on the same day are counted as two different dispensing events. |
Inhaler dispensing event |
Inhalers count as one dispensing event; for example, an inhaler with a 90-day supply is considered one dispensing event. In addition, multiple inhalers of the same medication filled on the same date of service should be counted as one dispensing event; for example a member may obtain two inhalers on the same day (one for home and one for work), but intend to use both during the same 30-day period. |
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
5–56 years by December 31 of the measurement year. Report three age stratifications and a total rate.
The total is the sum of the three numerators divided by the sum of the three denominators. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year and the year prior to the measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during each year of continuous enrollment. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage during each year of continuous enrollment year. |
Anchor date |
December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefits |
Medical. Pharmacy during the measurement year. |
Event/diagnosis |
Follow the steps below to identify the eligible population for the measure. |
Step 1 |
Identify members as having persistent asthma who met at least one of the four criteria below, during both the measurement year and the year prior to the measurement year (criteria need not be the same across both years).
|
Table ASM-A: Codes to Identify Asthma
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Asthma |
493 |
Table ASM-B: Codes to Identify Visit Type
Description |
CPT |
UB-92 Revenue |
Outpatient |
99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99217-99220, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99382-99386, 99392-99396, 99401-99404, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429, 99499 |
051x, 052x, 057x- 059x, 077x, 0982, 0983 |
Acute inpatient |
99221-99223, 99231-99233, 99238, 99239, 99251-99255, 99261-99263, 99291 |
010x, 0110-0114, 0119, 0120-0124, 0129, 0130-0134, 0139, 0140-0144, 0149, 0150-0154, 0159, 016x, 020x-022x, 072x, 0987 |
Emergency department |
99281-99285 |
045x, 0981 |
Table ASM-C: Asthma Medications
Description |
Prescriptions |
|||
Preferred therapy |
|
|
|
|
Add-on therapy |
|
|
||
Note: NCQA will provide a comprehensive list of NDC codes for the appropriate numerator and denominator asthma medications on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Step 2 |
For a member identified as having persistent asthma because of at least four asthma medication dispensing events (Table ASM-C), where leukotriene modifiers were the sole asthma medication dispensed, the member must:
|
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerator |
Dispensed at least one prescription for inhaled corticosteroids, nedocromil, cromolyn sodium, leukotriene modifiers or methylxanthines during the measurement year (Table ASM-C). |
Exclusion (optional)
Exclude from the eligible population all members diagnosed with emphysema or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) any time on or prior to December 31 of the measurement year, as identified by the following codes.
Table ASM-D: Codes to Identify Exclusions
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Emphysema |
492, 506.4, 518.1, 518.2 |
COPD |
491.2, 493.2, 496, 506.4 |
Note
The definition used for “persistent” asthma is a rough approximation based on the previous two years’ service and medication use rather than a clinical measure of severity. This definitional approach was chosen for logistical and feasibility reasons so that an efficient, reasonably standardized and sufficiently large population that allows unbiased MCO-to-MCO comparison could be identified through administrative sources.
The first four classes of medication in Table ASM-C count in the numerator because they are considered acceptable as primary therapy for long-term control of asthma. The last class (inhaled beta-2 agonists) does not count in the numerator because it is recommended as add-on rather than primary therapy for persistent asthma.
For public reporting, NCQA may weigh the three age stratifications based on national distributions and report as a single rate for each of the two product lines.
MCOs should allocate the dispensing events to the appropriate year based on the date the prescription is filled.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table ASM-1/2/3: Data Elements for Use of Appropriate Medications for People With Asthma
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
For each age stratification and total |
Numerator events by administrative data |
For each age stratification and total |
Reported rate |
For each age stratification and total |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
For each age stratification and total |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
For each age stratification and total |
Use of
Spirometry Testing in the Assessment
and Diagnosis of COPD
(SPR)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Clarified the Index Episode Start Date, the Negative Diagnosis History and the allowable gap criteria.
Description
The percentage of members 40 years of age and older with a new diagnosis or newly active chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who received appropriate spirometry testing to confirm the diagnosis (this measure identifies incident cases using a clean claim period).
Definitions
Index Episode Start Date |
The earliest encounter during the Intake Period with a qualifying diagnosis of COPD (Table SPR-A). For an outpatient episode, the Index Episode Start Date (IESD) is the date of service. For an inpatient episode, the IESD is the date of discharge. For a transfer or readmission, the IESD is the discharge date of original admission. |
Negative Diagnosis History |
A period of 730 days (2 years) prior to the Index Episode Start Date, during which the member had no claims/encounters containing any principal or secondary diagnosis of COPD (Table SPR-A). For an Inpatient Index Episode, use the date of admission to determine the Negative Diagnosis History. |
Intake Period |
A 12-month window that begins on July 1 of the year prior to the measurement year and ends on June 30 of the measurement year. The Intake Period is used to capture eligible episodes of treatment. |
New Episode |
To qualify as a New Episode, two criteria must be met.
|
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
42 years or older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
730 days (2 years) prior to the IESD through 180 days after the IESD. |
Allowable gap |
One gap in enrollment of up to 45 days is allowed in each of the 12-month periods prior to the IESD or in the 6-month period after the IESD, for a maximum of 2 gaps total. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage (i.e., a member whose coverage lapses for 2 months [60 days] is not considered continuously enrolled). |
Anchor date |
Index Episode Start Date. |
Benefit |
Medical. |
Event/diagnosis |
A new episode of COPD. Follow the steps below to identify the eligible population for the measure. |
Step 1 |
Identify all members who, during the Intake Period, had any diagnosis of COPD (Table SPR-A). |
Table SPR-A: Codes to Identify COPD
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Chronic bronchitis |
491 |
Emphysema |
492 |
COPD |
496 |
Step 2 |
Determine the COPD Episode Start Date. For each member identified in step 1, identify the date of the earliest encounter during the Intake Period with a COPD diagnosis (Table SPR-A). |
Step 3 |
Determine if the Episode Start Date is a New Episode. Members with a New Episode of COPD must have a Negative Diagnosis History. Members with any encounter or claim with a COPD diagnosis during the 730 days (2 years) prior to the Index Episode Start Date should be excluded from the denominator. For an inpatient index episode, use the date of admission to determine the Negative Diagnosis History. |
Step 4 |
Calculate continuous enrollment. Members must be continuously enrolled in the MCO 730 days (2 years) prior to the Episode Start Date through 180 days after the Episode Start Date. |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerator |
At least one claim/encounter with any code listed in Table SPR-B for spirometry in the 730 days (2 years) before to 180 days after the Episode Start Date. |
Table SPR-B: Codes to Identify Spirometry Testing
Description |
CPT |
Spirometry |
94010, 94014-94016, 94060, 94070, 94620 |
Data Elements
Table SPR-1/2/3: Data Elements for Use of Spirometry Testing in the Assessment and Diagnosis of COPD
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
|
Reported rate |
|
Lower 95% confidence interval |
|
Upper 95% confidence interval |
|
Follow-Up After Hospitalization for Mental Illness (FUH)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added HCPCS codes to Table FUH-B.
Added CPT code 99510 to FUH-B.
Description
The percentage of discharges for members 6 years of age and older who were hospitalized for treatment of selected mental health disorders and who were seen on an outpatient basis or were in intermediate treatment with a mental health provider.
Calculations
Six separate calculations are required—one for each of the three product lines for both of the following.
The percentage of discharges for members who had an outpatient or intermediate mental health visit on the date of discharge, up to 30 days after hospital discharge, and
The percentage of discharges for members who had an outpatient or intermediate mental health visit on the date of discharge, up to seven days after hospital discharge.
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
6 years and older as of the date of discharge. |
Continuous enrollment |
Date of discharge through 30 days after discharge. |
Allowable gap |
No gaps in enrollment. |
Anchor date |
None. |
Benefits |
Medical and mental health (inpatient and outpatient). |
Event/diagnosis |
Discharged from an inpatient setting of an acute care facility (including acute care psychiatric facilities) with a discharge date occurring on or before December 1 of the measurement year and a principal ICD-9-CM Diagnosis code indicating a mental health disorder specified in Table FUH-A. The MCO should not count discharges from nonacute care facilities (e.g., residential care or rehabilitation stays). |
Table FUH-A: Codes to Identify Mental Health Diagnosis
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
DRG |
295–299, 300.3, 300.4, 301, 308, 309, 311–314 |
426, 430 |
Multiple discharges
|
A member with more than one discharge on or before December 1 of the measurement year with a principal diagnosis of a mental health disorder (Table FUH-A) could be counted more than once in the eligible population. |
Mental health readmission or direct transfer |
If the discharge for a selected mental health disorder is followed by readmission or direct transfer to an acute facility for any mental health principal diagnosis within the 30-day follow-up period, count only the readmission discharge or the discharge from the facility to which the member was transferred. Although rehospitalization might not be for a selected mental health disorder, it is probably for a related condition. Only readmissions with a discharge date that occurs on or before December 1 of the measurement year are included in the measure. Refer to the ICD-9-CM codes listed in Table MIP-A. Exclude discharges followed by readmission or direct transfer to a nonacute facility for any mental health principal diagnosis within the 30-day follow-up period. These discharges are excluded from the measure because readmission or transfer may prevent an outpatient follow-up visit from taking place. (Refer to Table NON-A for codes to identify nonacute care.) |
Non-mental health readmission or direct transfer |
Exclude discharges in which the patient was transferred directly or readmitted within 30 days after discharge to an acute or nonacute facility for a non-mental health principal diagnosis. These discharges are excluded from the measure because rehospitalization or transfer may prevent an outpatient follow-up visit. |
Denied claims |
Denials of inpatient care (e.g., those resulting from members failing to get proper authorization) are not excluded from the measure. |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. Note: The eligible population for this measure is based on discharges, not members. It is possible for the denominator for this measure to contain multiple discharge records for the same individual. |
Numerators |
An outpatient mental health encounter or intermediate treatment with a mental health practitioner within the specified time period. For each denominator event (discharges), the follow-up visit must occur after the applicable discharge. An outpatient visit on the date of discharge should be included in the measure. |
Note: Refer to Appendix 3 for the definition of mental health practitioner.
30-day follow-up |
An outpatient follow-up encounter with a mental health practitioner up to 30 days after hospital discharge. To identify outpatient follow-up encounters, use the CPT codes or the UB-92 revenue codes in Table FUH-B. |
7-day follow-up |
An outpatient follow-up encounter with a mental health practitioner up to 7 days after hospital discharge. To identify outpatient follow-up encounters, use the CPT codes or the UB-92 revenue codes in Table FUH-B. |
Table FUH-B: Codes to Identify Outpatient Mental Health Encounters or Intermediate Treatment
Description |
CPT |
HCPCS |
UB-92 Revenue * |
Outpatient or intermediate care |
90801, 90802, 90804-90819, 90821-90824, 90826-90829, 90845, 90847, 90849, 90853, 90857, 90862, 90870, 90871, 90875-90876, 99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99383-99387, 99393-99397, 99401-99404, 99510 |
G0155, G0176, G0177, H0002, H0004, H0031, H0034-H0037, H0039, H0040, H2000, H2001, H2010-H2020, M0064, S9480, S9484, S9485 |
0513, 0900, 0901, 0905-0907, 0909-0916, 0961 |
* The MCO does not need to determine practitioner type for follow-up visits identified through UB-92 Revenue codes.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table FUH-1/2/3: Data Elements for Follow-Up After Hospitalization for Mental Illness
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
Each of the 2 rates |
Reported rate |
Each of the 2 rates |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 2 rates |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 2 rates |
Antidepressant Medication Management (AMM)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added HCPCS codes to Table AMM-B.
Description
The following components of this measure assess different facets of the successful pharmacological management of depression.
Optimal Practitioner Contacts for Medication Management. The percentage of members 18 years of age and older as of April 30 of the measurement year who were diagnosed with a new episode of depression and treated with antidepressant medication, and who had at least three follow-up contacts with a practitioner coded with a mental health diagnosis during the 84-day (12-week) Acute Treatment Phase. At least one of the three follow-up contacts must be with a prescribing practitioner.
Effective Acute Phase Treatment. The percentage of members 18 years of age and older as of April 30
of the measurement year who were diagnosed with a new episode of depression, were treated with antidepressant medication and remained on an antidepressant drug during the entire 84-day (12-week)
Acute Treatment Phase.Effective Continuation Phase Treatment. The percentage of members 18 years of age and older as of April 30 of the measurement year who were diagnosed with a new episode of depression and treated with anti-depressant medication and who remained on an antidepressant drug for at least 180 days.
Definitions
Intake Period |
The 12-month window starting on May 1 of the year prior to the measurement year and ending on April 30 of the measurement year. |
|
Index Episode Start Date |
The earliest encounter during the Intake Period with a qualifying diagnosis of major depression. |
|
Index Prescription Date |
The earliest prescription for antidepressants filled within a 44-day period, defined as 30 days prior to through 14 days on or after the Index Episode Start Date. |
|
Negative Diagnosis History |
A period of 120 days (4 months) prior to the Index Episode Start Date, during which time the member had no claims/encounters containing either a principal or secondary diagnosis of depression (Table AMM-A). |
|
Negative Medication History |
A period of 90 days (3 months) prior to the Index Prescription Date, during which time the member had no pharmacy claims for either new or refill prescriptions for a listed antidepressant drug (refer to the medication listing at the end of this measure specification). |
|
New Episode |
To qualify as a New Episode, two criteria must be met.
|
|
Treatment days |
The actual number of calendar days covered with prescriptions within the specified 180-day measurement interval. For Effective Continuation Phase Treatment, a prescription of 90 days supply dispensed on the 100th day will have 80 days counted in the 180-day interval. |
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
18 years and older as of April 30 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
120 days prior to the Index Episode Start Date through 245 days after the Index Episode Start Date. |
Allowable gap |
One gap in enrollment of up to 45 days. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage (i.e., a member whose coverage lapses for 2 months (60 days) is not considered continuously enrolled). |
Anchor date |
Index Episode Start Date. |
Benefits |
Medical, pharmacy and mental health (inpatient and outpatient). |
Event/diagnosis |
Diagnosed with a New Episode of major depressive disorder during the Intake Period and treated with antidepressant medication. Follow the steps below to identify the eligible population, which is the denominator for all three rates for this measure. |
Step 1 |
Identify all members with a diagnosis of depression who, during the 12-month Intake Period, had:
Note: Do not include lab claims when identifying members with depression. |
Table AMM-A: Codes to Identify Major Depression
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
DRG |
Major depression* |
296.2, 296.3, 298.0, 300.4, 309.1, 311 |
426** |
Prior depressive episodes |
296.2-296.9, 298.0, 300.4, 309.0, 309.1, 309.28, 311 |
426** |
* Brief depressive reaction (309.0) is not used for diagnosis, since it includes grief reaction (believed to be the most common use of that code). Additionally, other possible codes that could indicate depression diagnosis (296.4-296.9, 309.0, 309.28) are not included in this list because these codes are less specific in identifying eligible members.
** The MCO must exclude members with this code if the principal diagnosis is ICD-9-CM code 301.12.
Step 2 |
Determine the Index Episode Start Date and test for Negative Diagnosis History. For each member identified in step 1, determine the Index Episode Start Date by finding the date of the member’s earliest encounter during the Intake Period (i.e., outpatient or emergency room visit date, inpatient discharge date, partial hospitalization visit date) with a qualifying major depression diagnosis (Table AMM-A). Identify members who were diagnosed with a New Episode of depression. The range of ICD-9-CM Diagnosis codes for prior depressive episodes in Table AMM-A is more comprehensive to exclude members diagnosed with any type of depression. Members with any diagnosis of depression within the previous 120 days (4 months) of the Index Episode Start Date should be dropped from this denominator. |
Step 3 |
Identify members receiving antidepressant medication therapy. Among members identified in step 2, find those who filled a prescription for an antidepressant medication within 30 days before the Index Episode Start Date to 14 days on or after the Index Episode Start Date. |
Step 4 |
Calculate
continuous enrollment. Members must be continuously
enrolled in |
Step 5 |
Identify the Index Prescription Date. Identify the earliest prescription up to 30 days before the Index Episode Start Date to 14 days on or after the Index Episode Start Date. Prescriptions may be up to 30 days before the Index Episode Start Date to account for members having a recurrent episode who may be started on medication based on a phone encounter while awaiting a scheduled office visit. Similarly, prescriptions may be 14 days on or after the Index Episode Start Date to account for either clinical discretion in recommending a 2-week trial of self-help techniques prior to starting on medication or for member delay in filling the initial prescription. |
Step 6 |
From the resulting members from step 5, confirm the New Episode by testing for a Negative Medication History. Members who have antidepressant prescriptions filled during the Negative Medication History period do not represent new treatment episodes and must be excluded. |
Step 7 |
Exclude members who had an acute inpatient stay with a principal diagnosis of mental health or substance abuse during the 245 days after the Index Episode Start Date treatment period. Use the codes provided in the Use of Services Domain to identify acute mental health or substance abuse inpatient hospitalizations (Tables MIP-A, CIP-A). |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerators |
|
Optimal practitioner contacts for medication management |
Three
or more outpatient follow-up visits or intermediate treatment with
a practitioner (at least one of which is a prescribing
practitioner) within the 84-day |
|
Identify all members in the denominator population who had:
Do not count the Index Episode Start Date visit in cases where the member had two visits with a secondary diagnosis of depression. The MCO may include the second visit with a secondary diagnosis of depression toward the optimal contacts rate. Emergency room visits do not count toward the numerator. Visits with mental health practitioners: To identify visits with mental health practitioners, use any of the CPT or UB-92 Revenue codes in Table AMM-B. Visits with non-mental health practitioners: To identify visits with non-mental health practitioners, use:
|
Table AMM-B: Codes to Identify Follow-Up Office Visits
Description |
CPT |
HCPCS |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
UB-92 Revenue |
Psychiatric visit codes |
90801, 90802, 90804-90819, 90821-90824, 90826-90829, 90845, 90847, 90849, 90853, 90857, 90862, 90870, 90871, 90875, 90876 |
G0155, G0176, G0177, H0002, H0004, H0031, H0034, H0036, H0037, H0039, H0040, H2000, H2010, H2011, H2013-H2020, M0064, S9484, S9485 |
|
0513, 0900, 0901, 0905-0907, 0909-0916, 0961 |
Evaluation and management codes |
99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99384-99387, 99394-99397, 99401-99404 |
|
290, 293-302, 306-316 |
|
Telephone visits |
99371-99373 |
|
290, 293-302, 306-316 |
|
|
The MCO must verify that at least one of the three follow-up visits was with a prescribing practitioner (this may be the telephone visit). Members who did not receive a follow-up visit within the 12-week Acute Treatment Phase with a prescribing practitioner are not counted in the numerator for Optimal Practitioner Contacts rate. |
Effective Acute Phase treatment |
An 84-day (12-week) acute treatment with antidepressant medication. Identify all members in the denominator population who filled a sufficient number of separate prescriptions/refills of antidepressant medication treatment to provide continuous treatment for at least 84 days. Continuous treatment allows gaps in medication treatment up to a total of 30 days during the 84-day period. Allowable medication changes or gaps include:
Regardless of the number of gaps, the total gap days may be no more than 30 days. The MCO may count any combination of gaps (e.g., two washout gaps, each 15 days, or two washout gaps of 10 days each and one treatment gap of 10 days). The total gap days may not exceed 30 days. To determine continuity of treatment during the 114-day period, sum the number of gap days to the number of treatment days for a maximum of 114 days (i.e., 84 treatment days + 30 gap days = 114 days). For all prescriptions filled within 114 days of the Index Prescription Date, the MCO should count treatment days on the Index Prescription Date and continue to count until a total of 84 treatment days has been established. Members whose gap days exceed 30 or who do not have 84 treatment days within 114 days after the Index Prescription Date are not counted in the numerator. Table AMM-C lists the types of antidepressant medications included in this measure. |
Table AMM-C: Antidepressant Medications
Prescriptions |
|
|
|
Note: NCQA will provide a complete list of medications that count toward this measure on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Effective Continuation Phase treatment |
A 180-day treatment with antidepressant medication. Identify all members in the denominator population who filled a sufficient number of separate prescriptions/refills of antidepressant medication treatment to provide continuous treatment for at least 180 days. The continuous treatment definition allows gaps in medication treatment up to a total of 51 days during the 180-day period. Allowable medication changes or gaps include:
Regardless of the number of gaps, the total gap days may be no more than 51 days. The MCO may count any combination of gaps (e.g., two washout gaps, each 25 days or two washout gaps of 10 days each and one treatment gap of 10 days). Total gap days may not exceed 51 days. To determine continuity of treatment during the 231-day period, sum the number of allowed gap days to the number of treatment days for a maximum of 231 days (i.e., 180 treatment days + 51 gap days = 231 days); identify all prescriptions filled within the 231 days of the Index Prescription Date. |
|
The MCO should count treatment days on the Index Prescription Date and continue to count until a total of 180 treatment days has been established. Members whose gap days exceed 51 or who do not have 180 treatment days within 231 days after the Index Prescription Date are not counted in the numerator. Table AMM-C lists the types of antidepressant medications included in this measure. |
Note
The intent of the telephone visit is that the exchange occurred between the patient and one of the practitioner types (mental health and non-mental health practitioners) that count for face-to-face visits. The MCO may not count contacts from other types of services (e.g., disease management, case management) toward the Optimal Practitioner Contacts measure.
If the member has a mental health or pharmacy benefit with the MCO (or if the MCO contracts with the mental health or pharmacy benefit with a separate vendor) and the claim for depression treatment or antidepressant medication is denied (e.g., the member failed to get proper authorization), the member should be included in the denominator of this measure.
A member with a mental health benefit whose claim for follow-up visits is denied is included in the denominator of this measure but must also meet all other eligibility requirements for inclusion.
Refer to Appendix 3 for the definition of mental health practitioner and prescribing practitioner.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table AMM-1/2/3: Data Elements for Antidepressant Medication Management
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
Each of the 3 rates |
Reported rate |
Each of the 3 rates |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 3 rates |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 3 rates |
Follow-Up Care
for Children Prescribed Attention-Deficit/
Hyperactivity
Disorder (ADHD) Medication (ADD)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Clarified the age criteria.
Added CPT codes 96101, 96116, 96118 to Table ADD-B.
Added HCPCS codes to Table ADD-B.
Revised Continuation and Maintenance (C&M) Phase eligible population criteria.
Description
The percentage of children newly prescribed ADHD medication who have at least 3 follow-up care visits within a 10-month period, one of which is within 30 days of when the first ADHD medication was dispensed. The following 2 rates in the measure assess follow-up care for children prescribed an ADHD medication:
Initiation Phase |
The percentage of members 6–12 years of age as of the Index Prescription Episode Start Date with an ambulatory prescription dispensed for ADHD medication, who had one follow-up visit with practitioner with prescribing authority during the 30-day Initiation Phase. |
Continuation and Maintenance (C&M) Phase |
The percentage of members 6–12 years of age as of the Index Prescription Episode Start Date with an ambulatory prescription dispensed for ADHD medication, who remained on the medication for at least 210 days and who, in addition to the visit in the Initiation Phase, had at least 2 follow-up visits with a practitioner within 270 days (9 months) after the Initiation Phase ended. |
Definitions
Intake Period |
The 12-month window starting March 1 of the year prior to the measurement year and ending February 28 of the measurement year. |
Negative Medication History |
A period of 120 days (4 months) prior to the Index Prescription Episode Start Date, during which time the member had no ADHD medications dispensed for either new or refill prescriptions (Table ADD-A). |
Index Prescription Start Date |
The earliest prescription dispensing date for an ADHD medication where the date is in the Intake Period and there is a Negative Medication History. |
Initiation Phase |
The 30 days following the Index Prescription Episode Start Date. |
C&M Phase |
The 31–300 days following the Index Prescription Episode Start Date (9 months). |
New Episode |
The member must have a 120-day (4-month) Negative Medication History on or before the Index Prescription Episode Start Date. |
Continuous Medication Treatment |
The number of medication treatment days during the 10-month follow-up period must be equal to or greater than 210 days (i.e., 300 treatment days – 90 gap days). |
Treatment days (covered days) |
The actual number of calendar days covered with prescriptions within the specified 300-day measurement interval (i.e., a prescription of 90 days’ supply dispensed on the 220th day will have 80 days counted in the 300-day interval). |
Eligible Population: Rate 1—Initiation Phase
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
Six years as of March 1 of the year prior to the measurement year to 12 years as of February 28 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
Members must be continuously enrolled in the MCO for 120 days (4 months) prior to the Index Prescription Episode Start Date through 30 days (1 month) after the Index Prescription Episode Start Date. |
Allowable gap |
None. |
Anchor date |
None. |
Benefits |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event |
The MCO should follow the steps below to identify the eligible population for the Initiation Phase. |
Step 1 |
Identify all children in the specified age range who were dispensed an ADHD medication during the 12-month Intake Period (Table ADD-A). |
Table ADD-A: ADHD Medications
Prescriptions |
|
|
|
Note: NCQA will provide a list of medications that count toward this measure on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Step 2 |
Determine the Index Prescription Start Date and test for a Negative Medication History. For each member identified in step 1, test each ADHD prescription for a Negative Medication History. The Index Prescription Episode Start Date is the dispensing date of the earliest ADHD prescription in the Intake Period with a Negative Medication History. |
Step 3 |
Calculate continuous enrollment. Members must be continuously enrolled for 120 days prior to the Index Prescription Episode Start Date through 30 days after the Index Prescription Episode Start Date. |
Step 4 |
Exclude members who had an acute inpatient stay with a principal diagnosis of mental health or substance abuse during the 30 days after the Index Prescription Start Date. Use the codes provided in the Use of Service Domain to identify acute mental health or substance abuse inpatient hospitalizations (Tables MIP-A, CIP-A). |
Administrative Specification: Rate 1—Initiation Phase
Denominator |
The Rate 1 eligible population. |
Numerator |
One outpatient follow-up visit with a practitioner with prescribing authority within 30 days after the Index Prescription Start Date. Use Table ADD-B to identify the follow-up visit. This must be a face-to-face visit with a practitioner. Note: Do not count a visit on the Index Prescription Start Date as the initiation follow-up visit. ED visits do not count toward the numerator. |
Table ADD-B: Codes to Identify Follow-Up Visits
CPT |
HCPCS |
90801, 90802, 90804-90815, 90845, 90847, 90849, 90853, 90857, 90862, 90875, 90876, 96100, 96101, 96110, 96111, 96115, 96116, 96118, 96150-96154, 99078, 99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99241-99245, 99341-99350, 99354-99355, 99383-99384, 99393-99394, 99401-99404 |
G0155, G0176, G0177, H0002, H0004, H0031, H0034, H0036, H0037, H0039, H0040, H2000, H2010, H2011, H2013-H2020, M0064, S9484, S9485 |
OR
UB-92 Revenue |
WITH |
UB-92 Type of Bill |
0510, 0513, 0515, 0517, 0519-0523, 0529, 0900, 0902, 0903, 0905, 0907, 0909, 0910, 0914-0916, 0918, 0919, 0961, 0982, 0983, 0988 |
13x, 71x, 73x, 76x |
Eligible Population: Rate 2—C&M Phase
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
Six years as of March 1 of the year prior to the measurement year to 12 years as of February 28 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
Members must be continuously enrolled in the MCO for 120 days (4 months) prior to the Index Prescription Episode Start Date and 300 days (10 months) after the Index Prescription Episode Start Date. |
Allowable gap |
One
45 day gap in enrollment between 31 days and 300 days after the
Index Prescription Start Date. To determine continuous enrollment
for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified
monthly, the member may not have more than a |
Anchor date |
None. |
Benefits |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event |
The MCO should follow the steps below to identify the eligible population for the C&M Phase. |
Step 1 |
Identify all members who meet the eligible population criteria for Rate 1—Initiation Phase. |
Step 2 |
Calculate continuous enrollment. Members must be continuously enrolled from 31 days (1 month) after the Index Prescription Start Date through 300 days (10 months) after the Index Prescription Start Date. |
Step 3 |
Calculate the continuous medication treatment. Using the members in step 2, determine if the member filled a sufficient number of prescriptions to provide continuous treatment for at least 210 days out of the 300 day period. The continuous medication treatment definition allows gaps in medication treatment, up to a total of 90 days during the 300-day (10-month) period. (This period spans the Initiation Phase [1 month] and the C&M Phase [9 months].) Allowable medication changes or gaps include:
Regardless of the number of gaps, the total gap days may be no more than 90. The organization may count any combination of gaps (e.g., 1 washout gap of 14 days and numerous weekend drug holidays). |
Step 4 |
Exclude members who had an acute inpatient stay with a principal diagnosis of mental health or substance abuse during the 300 days after the Index Prescription Start Date. Use the codes provided in the Use of Service domain to identify acute mental health or substance abuse inpatient hospitalizations (Tables MIP-A, CIP-A). |
Administrative Specification—Rate 2: C&M Phase
Denominator |
The Rate 2 eligible population. |
Numerator |
Identify all members who had:
One of the two visits (during days 31–300) may be a telephone visit with practitioner. Use Table ADD-B to identify follow-up visits and Table ADD-C to identify telephone visits. Note: ED visits do not count toward the numerator. |
Table ADD-C: Codes to Identify Telephone Visits
CPT |
99371-99373 |
Exclusions (optional)
Exclude from the eligible population all members diagnosed with narcolepsy, at any point in the member’s history, as identified by the code in Table ADD-D.
Table ADD-D: Code to Identify Exclusions
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Narcolepsy |
347 |
Note
Members who switch product lines between the Rate 1 and Rate 2 continuous enrollment periods should only be included in Rate 1.
Members who have multiple different overlapping prescriptions should count the overlap days once toward the days supplied.
Refer to Appendix 3 for the definition of mental health practitioner and prescribing practitioner.
Data Elements for Reporting
An organization that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table ADD-1/2: Data Elements for Follow-Up Care for Children Prescribed ADHD Medication
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative only) |
|
Eligible population |
Each of the 2 rates |
Total exclusions |
Each of the 2 rates |
Numerator events by administrative data |
Each of the 2 rates |
Reported rate |
Each of the 2 rates |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 2 rates |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
Each of the 2 rates |
Glaucoma Screening in Older Adults (GSO)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added HCPCS codes to Table GSO-A.
Changed exclusion criteria to include evidence of glaucoma at any point in member’s history.
Removed optional data element Total Exclusions from Table GSO-3.
Description
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years and older without a prior diagnosis of glaucoma or glaucoma suspect who received a glaucoma eye exam by an eye-care professional for early identification of persons with glaucomatous conditions. An eye-care professional is an ophthalmologist or optometrist.
Eligible Population
Product line |
Medicare. |
Age |
67 years and older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year and the year prior to the measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during each year of continuous enrollment. |
Anchor date |
December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefit |
Medical. |
Event/diagnosis |
None. |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerator |
One (or more) eye exams for glaucoma by an eye care professional (ophthalmologist or optometrist) during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. A member is considered to have had an eye exam for glaucoma if a submitted claim/encounter contains any code in Table GSO-A. |
Table GSO-A: Codes to Identify Glaucoma Screening Eye Exams
CPT |
HCPCS |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
ICD-9-CM Procedure |
92002, 92004, 92012, 92014, 92081-92083, 92135, 92140, 99202-99205, 99213-99215, 99242-99245 |
G0117, G0118 |
V80.1 |
95.02, 95.03, 95.26 |
Exclusion (optional)
The MCO may exclude members who had a prior diagnosis of glaucoma or glaucoma suspect. The MCO should look for evidence of glaucoma as far back as possible in the member’s history. Use the codes in Table GSO-B to identify members with diagnoses of glaucoma or glaucoma suspect in administrative data. The exclusion must have occurred on or before the end of the measurement year.
Table GSO-B: Codes to Identify Exclusions
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Glaucoma suspect |
365.0 |
Glaucoma |
365.1-365.9 |
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table GSO-3: Data Elements for Glaucoma Screening
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
|
Reported rate |
|
Lower 95% confidence interval |
|
Upper 95% confidence interval |
|
Use of Imaging Studies for Low Back Pain (LBP)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Clarified the age criteria.
Separated diagnosis and visit type codes into two tables (LBP-A, LBP-B).
Added ICD-9-CM Diagnosis code 722.32 to Table LBP-A.
Deleted ICD-9-CM Diagnosis codes 721.90, 722.6 from Table LBP-A.
Added CPT codes 99217–99220, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429 to Table LBP-B.
Deleted CPT codes 99354–99357, 99387, 99397 from Table LBP-B.
Added UB-92 Revenue codes 057x-059x, 077x to Table LBP-B.
Deleted UB-92 Revenue codes 050x, 053x from Table LBP-B.
Removed optional data element Total Exclusions from LBP-1/2.
Description
This measure assesses whether imaging studies (plain X-ray, MRI, CT scan) are overused in evaluating patients with acute low back pain.
Calculations
The measure is reported as an inverted rate [1 – (numerator/denominator)]. A higher score indicates appropriate treatment of low back pain (i.e., proportion for whom imaging studies did not occur).
Definitions
Episode Start Date |
The earliest outpatient or ED encounter (Table LBP-B) during the measurement year with a primary low back pain diagnosis (Table LBP-A). |
Negative Diagnosis History |
180 days (6 months) prior to the Episode Start Date during which time the member had no claims/encounters with any diagnosis of low back pain (Table LBP-A). |
New Episode |
The first claim/encounter during the measurement year that meets both criteria.
|
Eligible Population
Product line |
Commercial, Medicaid (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
Adults 18 years as of January 1 of the measurement year to 50 years as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
180 days prior to the Episode Start Date through 28 days after the Episode Start Date. |
Allowable gap |
No gaps in enrollment during the continuous enrollment period. |
Anchor date |
Episode Start Date. |
Benefit |
Medical. |
Event/diagnosis |
Low back pain. The MCO should use claims/encounter data to identify members with a new episode of low back pain. The MCO should follow the steps below to identify the eligible population for this measure. |
Step 1 |
Identify all members in the specified age range who had an outpatient or ED encounter with a principal diagnosis of low back pain between January 1 and December 3 of the measurement year. Use Table LBP-A to identify low back pain and Table LBP-B to identify visit type. A diagnosis code from Table LBP-A must be in conjunction with a visit type code in Table LBP-B. |
Table LBP-A: Codes to Identify Low Back Pain
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Low back pain |
721.3, 722.10, 722.32, 722.52, 722.93, 724.02, 724.2, 724.3, 724.5, 724.6, 724.70, 724.71, 724.79, 738.5, 739.3, 739.4, 846.0, 846.1, 846.2, 846.3, 846.8, 846.9, 847.2 |
Table LBP-B: Codes to Identify Visit Type
Description |
CPT |
UB-92 Revenue |
Outpatient |
98925-98929, 98940-98942, 99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99217-99220, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99385, 99386, 99395, 99396, 99401-99404, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429, 99455, 99456, 99499 |
051x, 052x, 057x-059x, 077x, 0982, 0983 |
Emergency department |
99281-99285 |
045x, 0981 |
Step 2 |
Determine the Episode Start Date for each member by identifying the date of the member’s earliest encounter (identified in step 1) during the measurement year. |
Step 3 |
Determine if the Episode Start Date is a New Episode. Members with a New Episode of low back pain must have a Negative Diagnosis History. Exclude members with any low back pain diagnosis during the 180 days (6 months) prior to the Episode Start Date. |
Step 4 |
Exclude members who have a diagnosis for which an imaging study in the presence of low back pain is clinically indicated. The MCO should use the codes from Table LBP-C to exclude members with the following diagnoses.
|
Table LBP-C: Codes to Identify Exclusions (Clinically
Appropriate Indications for
Low Back Imaging)
|
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Cancer |
140-208, 230-239 |
|
|
Trauma |
800-839, 850-854, 860-869, 905-909, 926.11, 926.12, 929, 952, 958-959 |
|
|
IV drug abuse |
304.0, 304.1x, 304.2x, 304.4x, 305.4x, 305.5x, 305.6x, 305.7x |
|
|
Neurologic impairment |
344.60, 729.2 |
|
Step 5 |
Calculate continuous enrollment. The member must be continuously enrolled without any gaps for 180 days prior to the Episode Start Date through 28 days after the Episode Start Date. |
||
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerator |
|
Imaging study |
An imaging study (plain x-ray, MRI, CT scan) conducted on the Episode Start Date or in the 28 days following the Episode Start Date. Table LBP-D lists imaging studies to count toward the numerator. A diagnosis code from Table LBP-A must be in conjunction with an imaging study code in Table LBP-D. |
Table LBP-D: Codes to Identify Imaging Studies
Description |
CPT |
UB-92 Revenue |
Imaging studies |
72010, 72020, 72052, 72100, 72110, 72114, 72120, 72131-72133, 72141, 72142, 72146-72149, 72156, 72158, 72200, 72202, 72220 |
0320, 0329, 0350, 0352, 0359, 0610, 0612, 0614, 0619, 0972 |
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table LBP-1/2: Data Elements for Use of Imaging Studies for Low Back Pain
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
|
Reported rate |
|
Lower 95% confidence interval |
|
Upper 95% confidence interval |
|
Disease
Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug Therapy
in Rheumatoid Arthritis
(ART)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Separated diagnosis and visit type codes into two tables (ART-A, ART-B).
Added CPT codes 99304–99310, 99315, 99316, 99318, 99324–99328, 99334–99337, 99455, 99456 to Table ART-B.
Deleted CPT codes 99351–99355 from Table ART-B.
Added UB-92 Revenue codes 0118, 0128, 0138, 0148, 0158, 019x, 066x to Table ART-B.
Deleted UB-92 Revenue codes 0456, 049x, 050x, 053x, 056x, 076x, 092x, 094x, 096x, 0972-0979, 0984–0986, 0988, 0989 from Table ART-B.
Added Abatacept and Rituximab to Table ART-C.
Added J codes to Table ART-C.
Deleted Occurrence code 10 from Table ART-D.
Description
This measure assesses whether patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis have had at least one ambulatory prescription dispensed for a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD).
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare (report each product line separately). |
Ages |
18 years and older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage (i.e., a member whose coverage lapses for 2 months [60 days] is not considered continuously enrolled). |
Anchor date |
None. |
Benefits |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event/diagnosis |
Two face-to-face physician encounters with different dates of service in an outpatient or nonacute inpatient setting on or between January 1 and November 30 of the measurement year with any diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. A diagnosis code from Table ART-A must be in conjunction with a visit type code in Table ART-B. |
Table ART-A: Codes to Identify Rheumatoid Arthritis
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
714.0, 714.1, 714.2, 714.81 |
Table ART-B: Codes to Identify Visit Type
Description |
CPT |
UB-92 Revenue |
Outpatient |
99201-99205, 99211-99215, 99241-99245, 99341-99345, 99347-99350, 99384-99387, 99394-99397, 99401-99404, 99411, 99412, 99420, 99429, 99455, 99456, 99499 |
051x, 052x, 057x-059x, 077x, 0982, 0983 |
Nonacute inpatient |
99301-99313, 99315, 99316, 99318, 99321-99328, 99331-99337 |
0118, 0128, 0138, 0148, 0158, 019x, 055x, 066x |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population |
Numerator |
Members who had at least one ambulatory prescription dispensed for a disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) during the measurement year. Table ART-C lists the DMARDs included in this measure. |
Table ART-C: DMARDs
|
|
|
|
* The MCO may use the listed J codes as these infused medications that may not be captured via NDC codes.
Note: NCQA will provide a list of NDC codes for medications on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Exclusions (optional)
Exclude from the denominator members who have a diagnosis code for pregnancy during the measurement year.
Exclude from the denominator members who have been diagnosed with HIV. The MCO should use administrative data to look for evidence of HIV diagnosis as far back as possible in the member’s history.
Table ART-D: Codes to Identify Exclusions
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Human immunodeficiency virus |
042, V08 |
Pregnancy |
630-677, V22, V23, V28 |
Data Elements for Reporting
MCOs that submit HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table ART-1/2/3: Data Elements for DMARD Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Total exclusions |
|
Number of numerator events by administrative data |
|
Reported rate |
|
Lower 95% confidence interval |
|
Upper 95% confidence interval |
|
Annual Monitoring for Patients on Persistent Medications (MPM)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added Amlodipine-benazepril, Candesartan+HCTZ, Enalapril-felodipine, Enalapril-diltiazem, Eprosartan+ HCTZ, Irbesartan+HCTZ, Olmesartan+HCTZ, Quinapril+HCTZ, Telmisartan+HCTZ, Valsartan+HCTZ to Table MPM-A.
Deleted LOINC codes 5919-6, 13451-0, 15051-6 from Table MPM-B (serum creatinine).
Added HCTZ/Captopril, HCTZ/Fosinopril, HCTZ/Hydralizaine, HCTZ/Quinapril, HCTZ/Telmisartan, HCTZ/ Triamterene to Table MPM-D.
Deleted Benzthiazide, Hydroflumethazide, Quinethazone, HCTZ/Guanethidine from Table MPM-D.
Added Carbatrol, Di-Phen, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol, Tegretol XR to Table MPM-E.
Deleted Diphenylan, Depacaine, Myoproic Acid from Table MPM-E.
Condensed Table MPM-Ea–Table MPM-Ed to make Table MPM-E.
Condensed Table MPM-Fa–Table MPM-Fd to make Table MPM-F.
Added CPT Code 80050 to Table MPM-H.
Deleted Tables MPM-I and MPM-J.
Description
The percentage of members 18 years of age and older who received at least a 180-days supply of ambulatory medication therapy for the selected therapeutic agent during the measurement year and at least one therapeutic monitoring event for the therapeutic agent in the measurement year.
For each product line, report each of the five rates separately and as a total rate.
Annual monitoring for members on angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB)
Annual monitoring for members on digoxin
Annual monitoring for members on diuretics
Annual monitoring for members on anticonvulsants
Annual monitoring for members on statins
Total rate (the sum of the five numerators divided by the sum of the five denominators)
Note: NCQA will provide a comprehensive list of NDC codes for drugs to identify members on persistent medications on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Eligible Population
Product lines |
Commercial, Medicaid, Medicare. |
Ages |
18 years and older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during each year of continuous enrollment. To determine continuous enrollment for a Medicaid beneficiary for whom enrollment is verified monthly, the member may not have more than a 1-month gap in coverage (i.e., a member whose coverage lapses for 2 months [60 days] is not considered continuously enrolled). |
Anchor date |
December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefits |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event/diagnosis |
Members on persistent medications—defined as members receiving at least a 180-days supply of ambulatory medication in the measurement year for any medication listed in the medications table for each of the five rates in the measure (Tables MPM-A, MPM-C, MPM-D, MPM-E, MPM-G). To determine continuity of treatment during the 365-day period, sum the number of treatment days (days supply from all the scripts filled during the year) for a total of 180 days. |
Administrative Specification
For each product line, report each of the five rates separately and as a combined rate. The total rate is the sum of the five numerators divided by the sum of the five denominators.
Rate 1: Annual Monitoring for Members on ACE Inhibitors or ARBs
Additional eligible population criteria |
The number of members in the eligible population who received at least a 180-days supply of any drug in Table MPM-A for ACE inhibitors or ARBs, including any combination products during the measurement year. Note: Members may switch therapy with any medication listed in Table MPM-A during the measurement year and have the days supply for those medications count toward the total 180-days supply (i.e., a member who received 90 days of ACE inhibitors and 90 days of ARBs meets the denominator definition for rate 1). |
Table MPM-A: Drugs to Identify Members on ACE Inhibitors or ARBs
Description |
Drugs |
|
ACE inhibitors |
|
|
ACE inhibitors—Combination products |
|
|
ARBs |
|
|
ARB—Combination products |
|
|
Numerator |
The
number of members with at least one serum potassium and
either a Note: The two tests do not need to occur on the same service date, only within the measurement year. |
Table MPM-B: Codes to Identify Physiologic Monitoring Tests
Description |
CPT |
LOINC |
Serum potassium (K+) |
84132, 80050, 80051, 80053, 80048, 80069 |
2824-1, 2823-3, 6298-4, 12812-4, 12813-2, 22760-3, 24320-4, 24321-2, 24322-0, 24323-8, 24326-1, 24362-6, 29349-8, 32713-0, 34548-8, 34554-6 |
WITH |
||
Serum creatinine (SCr) |
82565, 80050, 80053, 80048, 80069, 82575 |
2160-0, 2163-4, 2164-2, 11041-1, 11042-9, 12195-4, 13441-1, 13442-9, 13443-7, 13446-0, 13447-8, 13449-4, 13450-2, 14682-9, 16188-5, 16189-3, 21232-4, 24321-2, 24322-0, 24323-8, 24320-4, 24362-6, 26752-6, 33558-8, 34555-3, 35591-7, 35592-5, 35593-3, 35594-1, 38483-4 |
OR |
||
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) |
84520, 84525, 80050, 80053, 80048, 80069 |
3094-0, 6299-2, 11064-3, 11065-0, 12964-3, 12965-0, 12966-8, 14937-7, 24320-4, 24321-2, 24322-0, 24323-8, 24362-6 |
Rate 2: Annual Monitoring for Members on Digoxin
Additional eligible population criteria |
The number of members in the eligible population who received at least a 180-days supply of any drug in Table MPM-C for digoxin, including any combination products, during the measurement year. Note: Members may switch therapy within any medication listed in Table MPM-C during the measurement year and have the days supply for those medications count toward the total 180-days supply. |
Table MPM-C: Drugs to Identify Members on Digoxin
Description |
Drugs |
Digoxin and digoxin combination products |
Digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxicaps, Lanoxin) |
Numerator |
The number of members with at least one serum potassium and either a serum creatinine or a blood urea nitrogen therapeutic monitoring test in the measurement year (Table MPM-B). Note: The two tests do not need to occur on the same service date, only within the measurement year. |
Rate 3: Annual Monitoring for Members on Diuretics
Additional eligible population criteria |
The number of members in the eligible population who received at least a 180-days supply of any drug in Table MPM-D, including any combination products, during the measurement year. Note: Members may switch therapy within any medication listed in Table MPM-D during the measurement year and have the days supply for those medications count toward the total 180-days supply. |
Table MPM-D: Drugs to Identify Members on Diuretics
Description |
Drugs |
|
Thiazide diuretics |
|
|
Potassium sparing diuretics (includes aldosterone blockers/ antagonists) |
|
|
Potassium wasting diuretics, including loop diuretics |
|
|
Combination potassium sparing/ wasting diuretics |
|
|
Table MPM-D: Drugs to Identify Members on Diuretics (continued)
Description |
Drugs |
|
Diuretics—Combination products |
|
|
Numerator |
The number of members with at least one serum potassium and either a serum creatinine or a blood urea nitrogen therapeutic monitoring test in the measurement year (Table MPM-B). Note: The two tests do not need to occur on the same service date, only within the measurement year. |
Rate 4: Annual Monitoring for Members on Anticonvulsants
Additional eligible population criteria |
The number of members in the eligible population who received at least a 180-days supply for any anticonvulsant in Table MPM-E during the measurement year. Note: Members who are on multiple anticonvulsant drugs count toward the denominator multiple times if they meet the persistent medications criteria for each drug taken during the measurement year (i.e., a member who received at least 180 days of phenytoin and 180 days of valproic acid will be counted twice in the denominator for Rate 4, once for each drug. |
Table MPM-E: Drugs to Identify Members on Anticonvulsants
Description |
Drugs |
||
Phenobarbital |
|
||
Phenytoin |
|
|
|
Valproic acid/valproate (dipropylacetic acid) |
|
|
|
Carbamazepine |
|
|
|
Numerator |
The number of members with at least one drug serum concentration level monitoring test for the prescribed drug in the measurement year (Table MPM-F). If a member received only one type of anticonvulsant, the drug serum concentration level test must be for the specific drug taken as a persistent medication (i.e., a member on phenytoin received a drug serum test for phenytoin). |
|
If a member persistently received multiple types of anticonvulsants, each anticonvulsant medication and drug monitoring test combination is counted as a unique event (i.e., a member on both phenytoin and valproic acid with at least a 180-days supply for each drug in the measurement year must separately show evidence of receiving drug serum concentration tests for each drug [Table MPM-F] to be considered numerator-compliant for each drug). |
Table MPM-F: Codes to Identify Drug Serum Concentration Monitoring Tests
Description |
CPT |
LOINC |
Drug serum concentration for phenobarbital |
80184 |
3948-7, 3951-1, 10547-8, 14874-2, 34365-7 |
Drug serum concentration for phenytoin |
80185, 80186 |
3968-5, 3969-3, 14877-5, 32109-1, 34540-5 |
Drug serum concentration for valproic acid (dipropylacetic acid) |
80164 |
4086-5, 4087-3, 4088-1, 14946-8, 18489-5, 21590-5, 32119-0, 32283-4 |
Drug serum concentration for carbamazepine |
80156, 80157 |
3432-2, 3433-0, 9415-1, 14056-6, 14639-9, 18270-9, 29147-6, 29148-4, 32058-0, 32852-6, 34545-4 |
Rate 5: Annual Monitoring for Members on Statins (HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors)
Additional eligible population criteria |
The number of members in the eligible population who received at least a 180-days supply for any statin (HMG CoA reductase inhibitors) in Table MPM-G, including any combination product, during the measurement year. Note: Members may switch therapy within any medication listed in Table MPM-G during the measurement year and have the days supply for the medications count toward the total 180-days supply. |
Table MPM-G: Drugs to Identify Members on Statins
Description |
Drugs |
|
Statins (HMG CoA reductase inhibitors) |
|
|
Statin combination products |
|
|
Numerator |
The number of members with both an ALT and an AST liver enzyme test in the measurement year (Table MPM-H). A liver function panel (which includes both ALT and AST) stands alone as numerator compliant. |
Table MPM-H: Codes to Identify Liver Function Monitoring Tests
Description |
CPT |
LOINC |
Liver enzyme test (AST) |
84450 |
1920-8, 27344-1, 30239-8 |
Liver enzyme test (ALT) |
84460 |
1742-6, 1743-4, 1744-2 |
OR |
||
Liver function panel |
80050, 80053, 80076 |
24323-8, 24324-6, 24325-3 |
Exclusion (optional)
The MCO should exclude members from each eligible population rate who had an inpatient stay (acute or nonacute) in the measurement year. Exclude any visit with an inpatient facility code or use UB-92 Type of Bill codes and DRGs codes from Table IPU-A to identify inpatient care. Refer to Table NON-A for codes to identify nonacute care.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table MPM-1/2/3: Data Elements for Therapeutic Monitoring
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Total exclusions |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Numerator events by administrative data |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Reported rate |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 5 rates and total |
Drugs to Be Avoided in the Elderly (DAE)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
Added Butalbital, Chlordiazepoxide-Methscopolamine, Estinyl, Estrace, Estratab, Estropriate, Gynodiol, Nandrolone, Oxandrolone, Stanozolol, Testosterone to Table DAE-A.
Deleted Mesoridazine, Pemoline, Cyclandelate from Table DAE-A.
Description
This measure summarizes:
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age who received at least one drug to be avoided in the elderly .
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age who received at least two different drugs to be avoided by the elderly.
The first rate assesses the extent to which elderly members have had some exposure to potentially harmful drugs. The second rate further assesses if elderly members have been exposed to multiple harmful drugs—which puts the elderly at increased risk for patient safety and adverse drug events. For both rates, a lower rate represents better performance.
Eligible Population
Product line |
Medicare. |
Age |
65 years and older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during the measurement year. |
Anchor date |
Enrolled as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefits |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event/diagnosis |
None. |
Administrative Specification
Denominator |
The eligible population. |
Numerator 1 |
At least one prescription for any drug to be avoided in the elderly (Table DAE-A) during the measurement year. |
Numerator 2 |
At least two prescriptions of different drugs to be avoided in the elderly (Table DAE-A) during the measurement year. Note: Identify different drugs using the Multum ID field located in the NDC list on NCQA’s Web site at www.ncqa.org. |
Table DAE-A: Drugs to Be Avoided in the Elderly
Therapeutic Class/ Application |
Drugs |
||||
Antianxiety |
Meprobamate (Equagesic, Equanil, Miltown) |
||||
Antiemetic |
Trimethobenzamide (Tigan) |
||||
Analgesic |
Ketorolac (Tordal) |
||||
Antihistamine |
|
|
|||
Antipsychotic, typical |
|
|
|||
Amphetamine |
|
|
|||
Barbiturate |
|
|
|||
Long-acting benzodiazepine |
|
|
|||
Other long-acting benzodiazepine |
|
|
|||
Calcium channel blocker |
|
||||
Gastrointestinal antispasmodic |
|
|
|||
Belladonna alkaloids (includes combination drugs) |
|
|
|||
Skeletal muscle relaxant |
|
|
|||
Oral estrogen |
|
|
|
|
|
Oral hypoglycemic |
|
||||
Narcotic |
|
|
|||
Vasodilator |
|
|
|||
Table DAE-A: Drugs to Be Avoided in the Elderly (continued)
Therapeutic Class/ Application |
Drugs |
||
Others |
|
|
|
Note: NCQA will provide a list of NDC codes for drugs to be avoided on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table DAE-3: Data Elements for Drugs to Be Avoided in the Elderly
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
|
Numerator events by administrative data |
For each of the 2 rates |
Reported rate |
For each of the 2 rates |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 2 rates |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 2 rates |
Potentially Harmful Drug-Disease Interactions in the Elderly (DDE)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
First-year measure.
Description
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who have evidence of an underlying disease, condition or health concern and who were dispensed an ambulatory prescription for a contraindicated medication, concurrent with or after the diagnosis.
Report each of the three rates separately and as a total rate.
A history of falls and a prescription for tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics or sleep agents
Dementia and a prescription for tricyclic antidepressants or anticholinergic agents
Chronic renal failure and prescription for nonaspirin NSAIDs or Cox-2 Selective NSAIDs
Total rate (the sum of the three numerators divided by the sum of the three denominators)
Members with more than one disease or condition can appear in the measure multiple times (i.e., in each indicator for which they qualify).
Note: NCQA will provide a comprehensive list of NDC codes for drugs to identify members on persistent medications on its Web site at www.ncqa.org by November 15, 2006.
Eligible Population
Product line |
Medicare. |
Age |
67 years and older as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Continuous enrollment |
The measurement year and the year prior to the measurement year. |
Allowable gap |
No more than 1 gap in enrollment of up to 45 days during each year of continuous enrollment. |
Anchor date |
Enrolled as of December 31 of the measurement year. |
Benefit |
Medical and pharmacy. |
Event/diagnosis |
Members with at least one disease or condition or procedure in the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. (Refer to the Additional Eligible Population Criteria for each rate.) |
Definitions
First Episode |
The first diagnosis, procedure or prescription between January 1 of the year prior to the measurement year and December 1 of the measurement year. |
Start Date |
For an outpatient claim/encounter, the start date is the date of service. For an inpatient claim, the start date is the discharge date. For dispensed prescriptions, the start date is the dispense date. |
Administrative Specification
Report each rate separately and as a combined rate. The combined rate is the sum of the three numerators divided by the sum of the three denominators.
Rate 1: Drug-Disease Interactions—History of Falls + Tricyclic Antidepressants, Antipsychotics or Sleep Agents
Additional eligible population criteria |
An accidental fall or hip fracture in the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. Follow the steps below to identify the eligible population. |
Step 1 |
Identify members who had an accidental fall or hip fracture (Table DDE-A) during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. |
Table DDE-A: Codes to Identify Falls or Hip Fractures
Description |
CPT |
ICD-9-CM Procedure |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Falls |
|
|
E880, E884, E885.9, E887, E888 |
Hip fracture* |
27230, 27232, 27235, 27236, 27238, 27240, 27244-27246, 27248, 27254 |
V54.13 |
820 |
*Hip fracture may be used as a proxy for identifying falls.
Step 2 |
Identify the First Episode. |
Step 3 |
Exclude members with a diagnosis of psychosis (Table DDE-B) during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. |
Table DDE-B: Codes to Identify Psychosis
Description |
ICD-9-CM Codes |
Dementias (with delirium or delusions) |
290.11, 290.12, 290.20, 290.3, 290.41, 290.42, 290.8, 290.9 |
Transient mental disorders due to conditions classified elsewhere |
293 |
Dementia in conditions classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance |
294.11 |
Schizophrenic disorders |
295 |
Episodic mood disorders with psychotic behavior |
296.x4 |
Delusional disorders |
297 |
Other nonorganic psychoses |
298 |
Numerator |
Dispensed an ambulatory prescription for a tricyclic antidepressant (Table DDE-C), antipsychotic or sleep agent (Table DDE-D) on or between the Start Date and December 31 of the measurement year. |
Table DDE-C: Tricyclic Antidepressants
|
|
|
|
Table DDE-D: Antipsychotics and Sleep Agents
Description |
Drugs |
|||
Antipsychotics |
|
|
|
|
Sleep agents |
|
|
|
|
Rate 2:
Drug-Disease Interactions-Dementia + Tricyclic Antidepressants or
Anticholinergic Agents
Additional eligible population criteria |
A diagnosis of dementia or a dispensed dementia medication during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year (Table DDE-E). Identify the First Episode for each member. |
Table DDE-E: Codes and Medications to Identify Dementia
Description |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
Dementia Medications |
|
Dementia |
290, 291.2, 292.82, 294.1 |
|
|
Organic brain syndrome |
294.8, 294.0 |
||
Alzheimer’s disease |
331.0 |
||
Frontotemperol dementia |
331.1x |
||
Dementia with Lewy bodies |
331.82 |
||
Numerator |
Dispensed an ambulatory prescription for a tricyclic antidepressant (Table DDE-C), or anticholinergic agent (Table DDE-F) on or between the Start Date and December 31 of the measurement year. |
Table DDE-F: Anticholinergic Agents
Description |
Drugs |
||
Antihistamines |
|
|
|
Antispasmodics |
|
|
|
Antivertigo/Antiematic |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle relaxants |
|
|
|
Anti-Parkinson’s |
|
|
|
Rate 3: Drug-Disease Interactions-Chronic Renal Failure + Nonaspirin NSAIDs or Cox-2 Selective NSAIDs
Additional eligible population criteria |
A diagnosis of chronic renal failure (Table DDE-G) during the measurement year or the year prior to the measurement year. Identify the First Episode for each member. |
Table DDE-G: Codes to Identify Chronic Renal Failure
Description |
CPT |
HCPCS |
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis |
ICD-9-CM Procedure |
UB-92 Revenue |
DRG |
Chronic renal failure |
36145, 36800, 36810, 36815, 36818, 36819-36821, 36831-36833, 50300, 50320, 50340, 50360, 50365, 50370, 50380, 90921, 90925, 90935, 90937, 90939, 90940, 90945, 90947, 90989, 90993, 90997, 90999, 99512 |
G0257, G0317-G0319, G0323, G0327, S9339 |
585.5, 585.6, V42.0, V45.1, V56 |
38.95, 39.27, 39.42, 39.43, 39.53, 39.93-39.95, 54.98, 55.6 |
0367, 080x, 082x-085x, 088x |
317 |
Numerator |
Dispensed an ambulatory prescription for an NSAID or Cox-2 selective NSAID (Table DDE-H) on or between the Episode Date and December 31 of the measurement year. |
Table DDE-H: NSAIDs and Cox-2 Selective NSAIDs
Description |
Drugs |
|||
NSAIDs |
|
|
|
|
Cox-2 selective NSAIDs |
|
|
|
|
Data Elements for Reporting
An MCO that submits HEDIS data to NCQA must provide the following data elements.
Table DDE-3: Data Elements for Potentially Harmful Drug-Disease Interactions in the Elderly
|
Administrative |
Measurement year |
|
Data collection methodology (administrative) |
|
Eligible population |
For each of the 3 rates and total |
Numerator events by administrative data |
For each of the 3 rates and total |
Reported rate |
For each of the 3 rates and total |
Lower 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 3 rates and total |
Upper 95% confidence interval |
For each of the 3 rates and total |
Medical Assistance With Smoking Cessation (MSC)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 3: Specifications for Survey Measures.
Description
The following components of this measure assess different facets of providing medical assistance with smoking cessation.
Advising
Smokers |
A rolling average represents the percentage of members 18 years of age and older who are current smokers, who were seen by an MCO practitioner during the measurement year and who received advice to quit smoking. |
Discussing Smoking Cessation Medications |
A rolling average represents the percentage of members 18 years of age and older who are current smokers, who were seen by an MCO practitioner during the measurement year and for whom smoking cessation medications were recommended or discussed. |
Discussing Smoking Cessation Strategies |
A rolling average represents the percentage of members 18 years of age and older who are current smokers, who were seen by an MCO practitioner during the measurement year and for whom smoking cessation methods or strategies were recommended or discussed. |
Flu Shots for Adults Ages 50–64 (FSA)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 3: Specifications for Survey Measures.
Description
The percentage of commercial members 50–64 years of age as of September 1 of the measurement year who received an influenza vaccination between September 1 of the measurement year and the date on which the CAHPS Health Plan Survey 4.0H, Adult Version was completed.
Flu Shots for Older Adults (FSO)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 3: Specifications for Survey Measures.
Description
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older as of January 1 of the measurement year who received an influenza vaccination between September 1 of the measurement year and the date on which the Medicare CAHPS survey was completed.
Pneumonia Vaccination Status for Older Adults (PNU)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 3: Specifications for Survey Measures.
Description
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older as of January 1 of the measurement year who have ever received a pneumococcal vaccine.
The Medicare Health Outcomes Survey (HOS)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 6: Specifications for the Medicare Health Outcomes Survey.
Description
This measure provides a general indication of how well a Medicare MCO manages the physical and mental health of its members. The survey measures each member’s physical and mental health status at the beginning and the end of a two-year period.
A two-year change score is calculated and each member’s physical and mental health status is categorized as better, the same or worse than expected, taking into account risk adjustment factors. MCO-specific results are assigned as percentages of members whose health status was better, the same or worse than expected.
Management of Urinary Incontinence in Older Adults (MUI)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 6: Specifications for the Medicare Health Outcomes Survey.
Description
The following components of this measure assess the management of urinary incontinence in older adults.
Discussing Urinary Incontinence |
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who reported having a problem with urine leakage in the past six months and who discussed their urine leakage problem with their current practitioner. |
Receiving Urinary Incontinence Treatment |
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who reported having a urine leakage problem in the past six months and who received treatment for their current urine leakage problem. |
Physical Activity in Older Adults (PAO)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 6: Specifications for the Medicare Health Outcomes Survey.
Description
The following components of this measure assess different facets of promoting physical activity in older adults.
Discussing Physical Activity |
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who had a doctor’s visit in the past 12 months and who spoke with a doctor or other health provider about their level of exercise or physical activity. |
Advising Physical Activity |
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who had a doctor’s visit in the past 12 months and who received advice to start, increase or maintain their level exercise or physical activity. |
Fall Risk Management (FRM)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 6: Specifications for the Medicare Health Outcomes Survey.
Description
The following components of this measure assess different facets of fall risk management.
Discussing Fall Risk |
The percentage of Medicare members:
who were seen by an MCO practitioner in the past 12 months and who discussed falls or problems with balance or walking with their current practitioner. |
Managing Fall Risk |
The percentage of Medicare members 65 years of age and older who had a fall or had problems with balance or walking in the past 12 months, who were seen by an MCO practitioner in the past 12 months and who received fall risk intervention from their current practitioner.
|
Osteoporosis Testing in Older Women (OTO)
Summary of Changes to HEDIS 2007
This measure is collected using survey methodology. Detailed specifications and summary of changes are contained in HEDIS 2007, Volume 6: Specifications for the Medicare Health Outcomes Survey.
Description
This measure assesses the number of Medicare women 65 years of age and older who report ever having received a bone density test to check for osteoporosis.
HEDIS 2007, Volume 2
| File Type | application/msword |
| File Title | EOC |
| Author | Lacourci |
| Last Modified By | CMS |
| File Modified | 2007-01-31 |
| File Created | 2007-01-31 |
© 2026 OMB.report | Privacy Policy